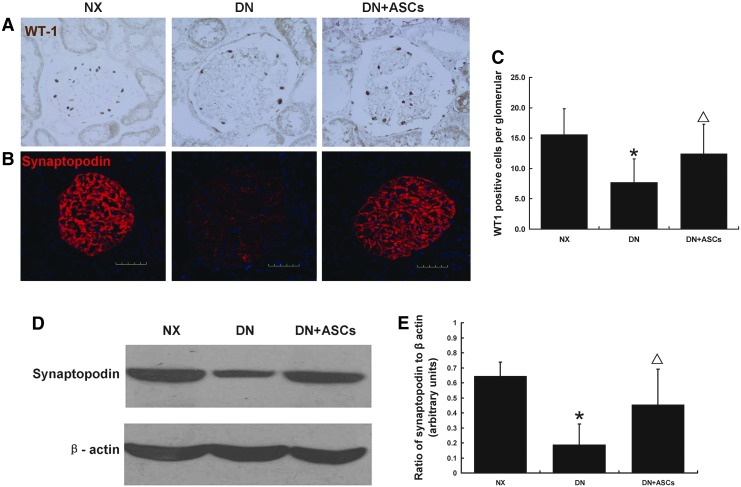
FIG. 4.
Effects of ASC treatment on podocyte injury in diabetic rats. Nuclear staining for the podocyte marker WT1, a transcription factor involved in podocyte differentiation and maintenance of a mature podocyte phenotype, in control and diabetic rats showed a reduction in WT-1-positive nuclei number per glomerulus in DN rats; this decrease was inhibited by ASC treatment (A, C). Immunofluorescent staining for synaptopodin protein in nephrectomy control (NX), DN, and DN+ASCs groups at 32 weeks after diabetes induction revealed a significant decrease in glomerular synaptopodin expression in DM rats. The decrease in synaptopodin expression in diabetic glomeruli was ameliorated by ASC treatment (B). This result was confirmed by western blotting (D, E). Original magnification, 400×. Data are means±SD (n=8–9). *P<0.05 versus NX; ▵P<0.05 versus DN.