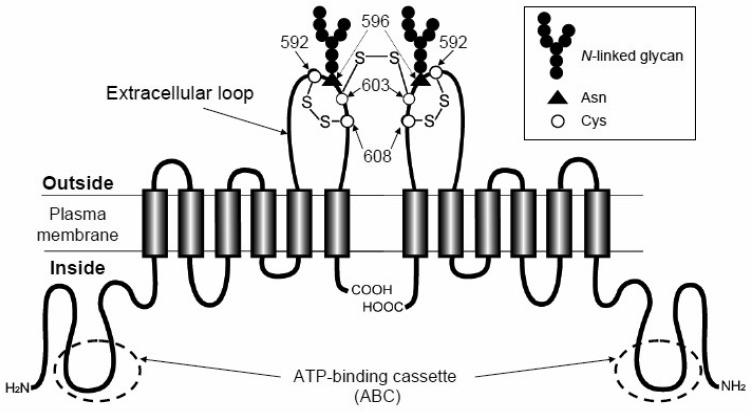
Figure 4.
Schematic illustrations of ABCG2 protein structure. The ABCG2 protein expressed in the plasma membrane is a homodimer linked via a cysteinyl disulfide bond. The cysteine residue corresponding to Cys603 of human ABCG2 is involved in homodimer formation. The substrate-binding site is formed when ATP is bound to the ATP-binding cassettes (ABC) of the ABCG2 homodimer. Disulfide bond formation at Cys603 does not appear to be prerequisite for exerting the transport activity of ABCG2.