Fig 1. Comparison of differential gene expression, RXRα binding genes, and binding motif between fenretinide- and ATRA-treated Huh7 cells.
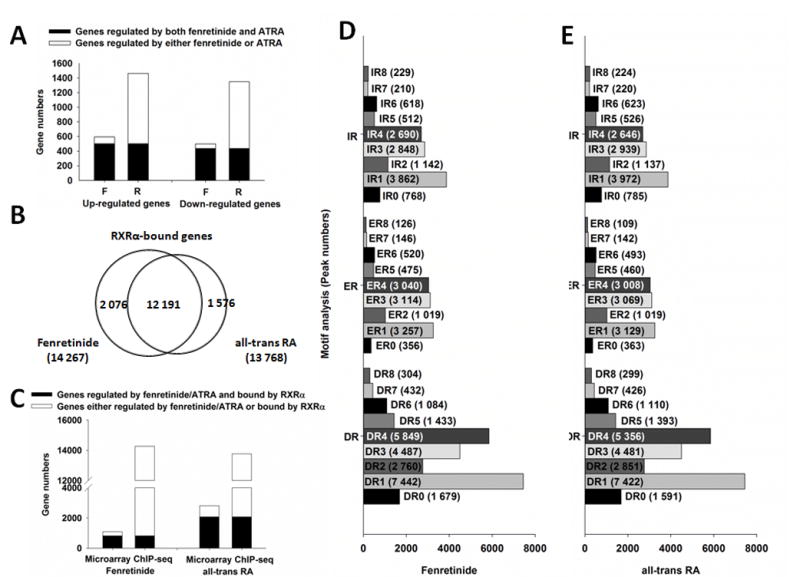
(A) Comparison of fenretinide and all-trans RA based on gene expression. F: fenretinide; R: all-trans RA. (B) Comparison of RXRα binding genes between fenretinide and all-trans RA. (C) Comparison of genes bound by RXRα and regulated by fenretinide and all-trans RA. (D) Motif analysis for genes bound by RXRα and regulated by fenretinide. (E) Motif analysis for genes bound by RXRα and regulated by all-trans RA. For gene expression analysis, total RNA was extracted from Huh7 cells after 12 hrs of fenretinide (10 μM), ATRA (10 μM) or DMSO (control) treatment, followed by microarray analyses. For RXRα binding and motif analysis, Huh7 cells were treated with fenretinide (10 μM) or ATRA (10 μM) for 3 hrs and then subjected to ChIP-Seq assay using IgG (negative control) or anti-RXRα antibody. Global profiling of RXRα binding motifs in Huh-7 cells were predicted by HiddenMarkov Model. DR: direct repeat; ER: everted repeat; IR: inverted repeat.
