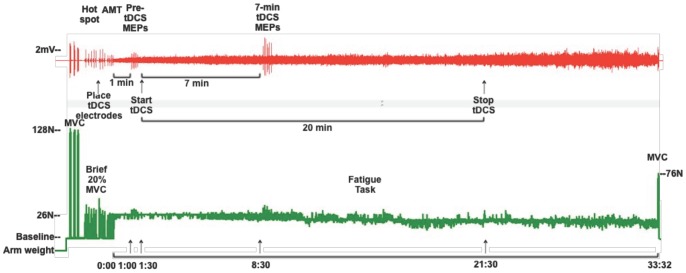
Figure 1. Experimental protocol.
(Top) Representative traces of biceps electromyogram (EMG) and (Bottom) force signal from one subject during anodal tDCS. Resting arm weight was measured and added as a constant to the force signal to create a 0.0N baseline with the arm relaxed. Three elbow flexion maximum voluntary contractions (MVCs) were followed by a series of brief (3–5 sec) 20%MVC contractions during which motor evoked potentials (MEPs) were measured in the biceps EMG. After locating the biceps motor hotspot, but prior to determining active motor threshold (AMT), the transcranial direct current (tDCS) electrodes were placed on the scalp. One minute after starting the fatigue task, 6 MEPs were evoked over 30 seconds (Pre-tDCS MEPs), immediately after which the anodal tDCS was initiated (at time 1∶30). The second set of 6 MEPs were evoked at time 8∶30 of the fatigue task which was after 7 minutes of tDCS (7-min tDCS MEPs). At time 21∶30 of the fatigue task, the tDCS stimulation was terminated as the maximum duration for the tDCS protocol was 20 minutes. This subject’s time to task failure was 33∶32 minutes. At task failure, one final MVC was performed prior to relaxing.