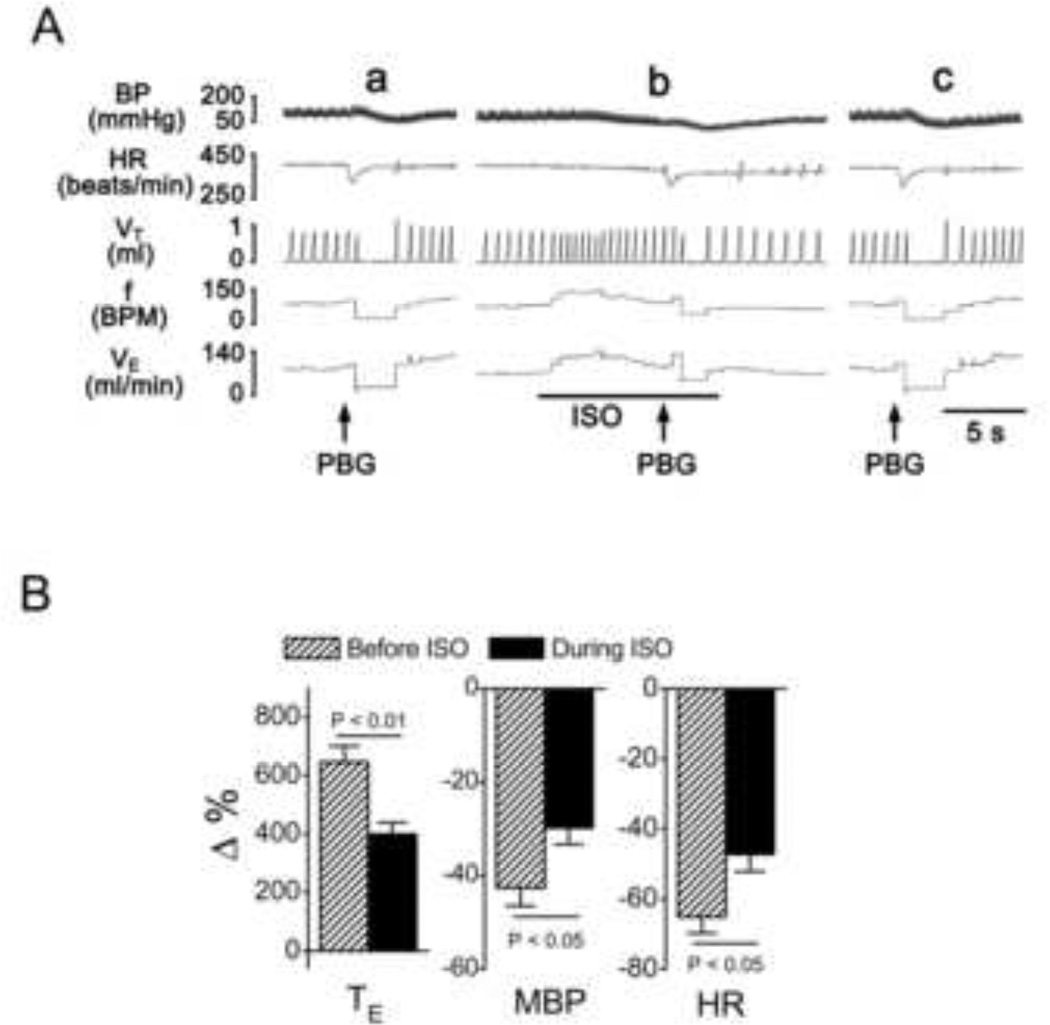
Fig. 1.
The effect of isoflurane (ISO) on PBG-induced apnea. A: Representative recordings showing apneic responses to PBG before (a), during (b) and 20 min after 5% ISO (c). Traces from top to bottom are arterial blood pressure, BP; heart rate, HR; tidal volume, VT; respiratory frequency (BPM = breaths/min), f; and minute ventilation, VE. B: Group data showing the effect of ISO on the PBG-induced cardiorespiratory changes. TE, expiratory duration; MBP, mean arterial blood pressure; HR, heart rate. N = 8, means ± SE.