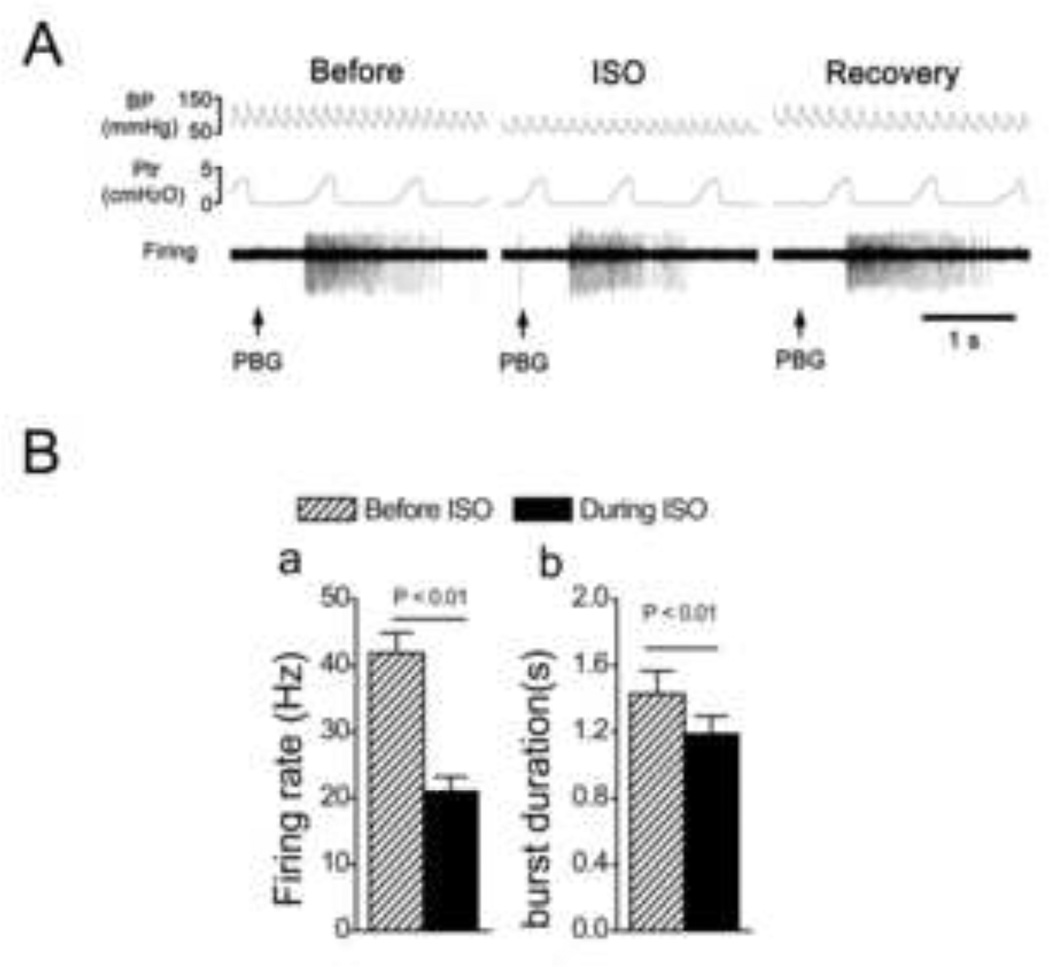
Fig. 2.
The effects of isoflurane (ISO) on the PBG-induced bursts in pulmonary C-type neurons. A: A representative recording showing that the bursting response to intra-atrium injection of PBG was attenuated by ISO in a pulmonary C-type neuron (the conduction velocity = 1.01 m/s). Traces from top to bottom are arterial blood pressure, BP; tracheal pressure, Ptr; and the cell’s activity, firing. B: Group data showing that ISO decreased the firing rate (a) and duration (b) of the PBG-induced bursts. N = 13, means ± SE.