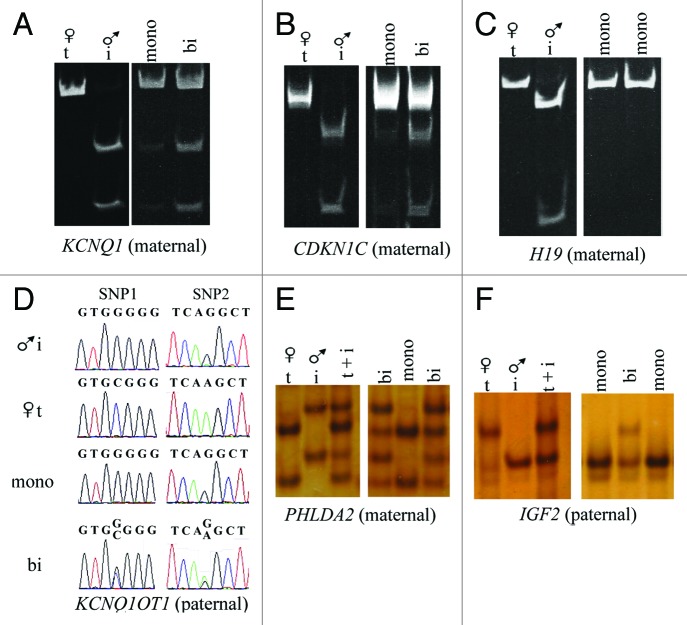
Figure 2. Example of assays used to determine allelic expression in tissues from B. t. indicus × B. t. taurus F1 hybrid conceptuses. Shown are examples of allelic determination by RT-PCR followed by RFLP and PAGE (A-C), Sanger sequencing (D) or SSCP analysis (E-F). The left portion of the panels (A-C, E and F) shows the band pattern of B. t. taurus and B. t. indicus control tissues (liver) which was used as reference to determine parental expression of imprinted gene in tissues from B. t. indicus × B. t. taurus F1 hybrids. The right portion of the panels shows examples of monoallelic and biallelic expression of several imprinted genes in ~d105 conceptus. (D) is an example of the Sanger sequencing allelic assay for KCNQ1OT1, a paternally-expressed gene. Two SNPs were used in this assay; double peaks demonstrate biallelic expression. The contribution of each parental allele to the total expression was determined by the use of Image J (NIH). Only samples with at least 10% expression from the repressed allele were considered to be biallelically-expressed. T, B. t. taurus; i, B. t. indicus; mono, monoallelic; bi, biallelic; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; RFLP, restriction fragment length polymorphism; SSCP, single strand conformation polymorphism; PAGE, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.