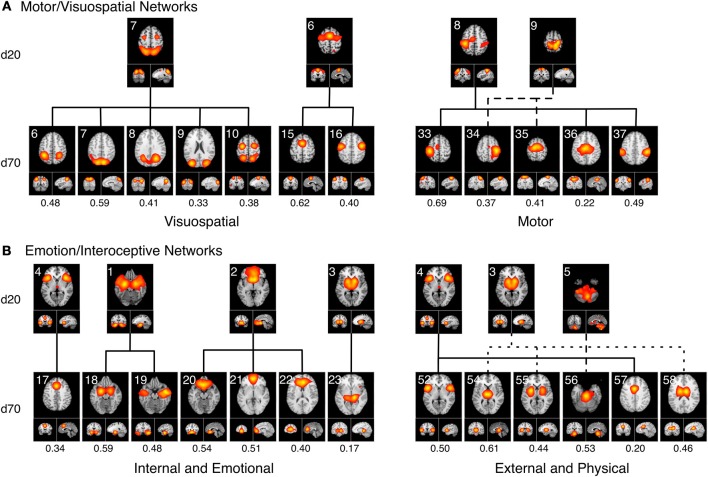
Figure 7.
Topological fractionation of select BrainMap-based ICNs are shown from low (d = 20) to high (d = 70) model orders. The spatial cross correlation between the d = 20 and d = 70 networks are indicated below each respective d = 70 network. (A) The Motor/Visuospatial networks, which were grouped into one cluster at d = 20 (green ICNs in Figure 6), split into three separate clusters at d = 70. Metadata associated with these ICNs indicated that two clusters were more closely related to visuospatial tasks while the other cluster was highly linked motor tasks. (B) The Emotion/Interoception networks (blue ICNs in Figure 6) showed a more complex fractionation at d = 70 when splitting into two main clusters. Both of these clusters contained sub-networks from nearly all of their d = 20 ICNs; however, the metadata associated with these d = 70 ICNs showed a clear division in functional characterization into an initial cluster linked to internal and emotional processes and another cluster linked to external and physical processes.