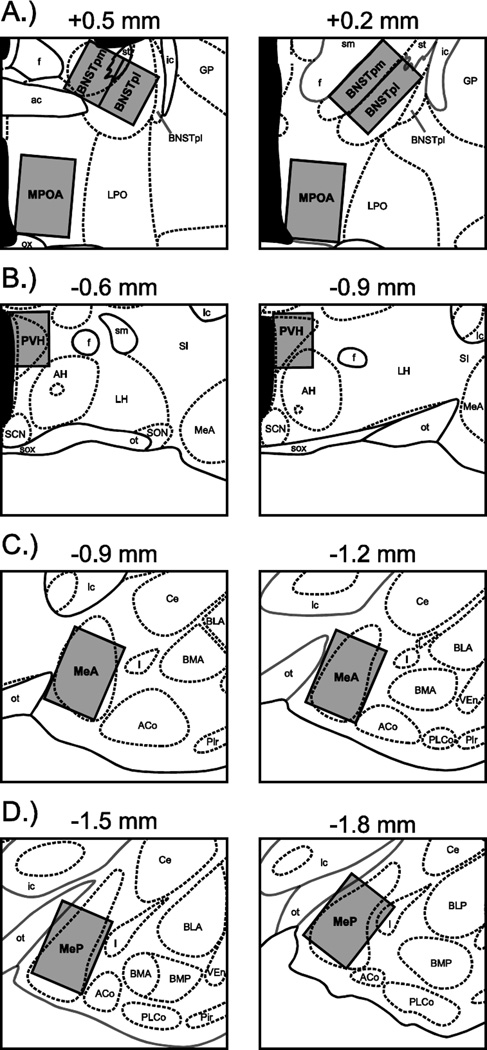
Figure 2.
Counting domains for quantifying oxytocin- and Fos-positive cells. Domains (gray boxes) were fitted to the following areas: (A) the posteromedial (BNSTpm) and posterointermediate (BNSTpi) subdivisions of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, and the medial preoptic area (MPOA), (B) the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVH), (C) the anterior division of the medial amygdala (MeA), and (D) the posterior division of the medial amygdala (MeP). Atlas plates are modified from Morin and Wood (2001), and arranged in distances relative to bregma. ac, anterior commissure; ACo, anterior cortical amygdaloid nucleus; AH, anterior hypothalamus; BLA, anterior division of the basolateral amygdaloid nucleus; BLP, posterior division of the basolateral amygdaloid nucleus; BMA, anterior division of the basomedial amygdaloid nucleus; BMP, posterior division of the basomedial amygdaloid nucleus; BNSTpl, posterolateral subdivision of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; Ce, central amygdaloid nucleus; f, fornix; GP, globus pallidus; I, intercalated nuclei of the amygdala; ic, internal capsule; LH, lateral hypothalamus; LPO, lateral preoptic area; ot, optic tract; ox, optic chiasm; Pir, piriform cortex; PLCo, posterolateral cortical amygdaloid nucleus; SCN, superchiasmatic nucleus; SI, substantia innominata, sm, stria medullaris; SON, supraoptic nucleus; sox, supraoptic decussation; st, stria terminalis; VEn, ventral endopiriform nucleus.