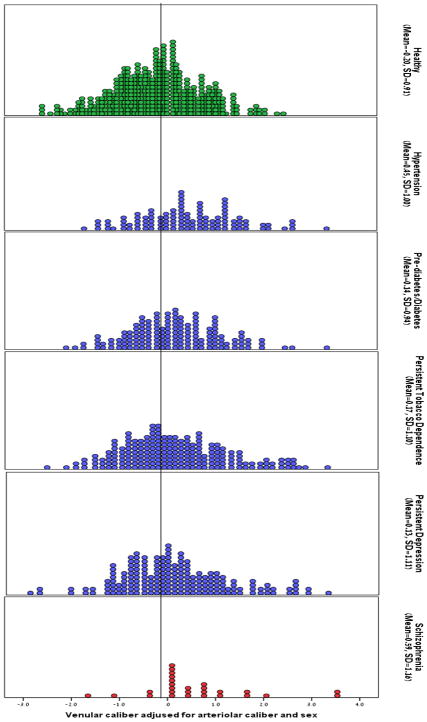
Figure 2.
Distribution of retinal venular caliber for the healthy, hypertension, pre-diabetes/diabetes, persistent tobacco dependence, persistent depression, and schizophrenia groups. Scores were adjusted for arteriolar caliber and sex and standardized (M=0.00, SD=1.00) on the population-representative cohort. The vertical line represents the mean for the healthy group. Both parametric and nonparametric statistical analyses showed that individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia had significantly wider venules – a finding that does not depend on extreme values.