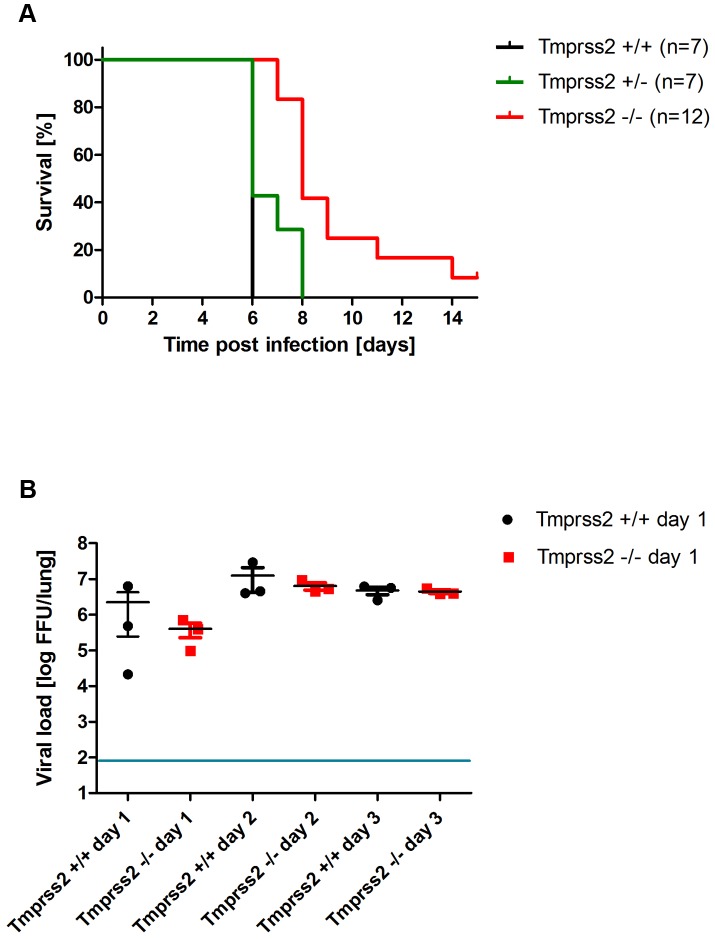
Figure 7. Tmprss2 knock-out mice show reduced mortality after infection with high dose H3N2 influenza A virus infections.
Eight to eleven weeks old female mice were infected with 2×103 FFU mouse-adapted H3N2 influenza virus by intra-nasal application and survival (A) was monitored until day 14 p.i. In addition to mice that were found dead, mice with a weight loss of more than 30% of the starting body weight were euthanized and recorded as dead. Infectious viral particles were determined in lung homogenates (B). Individual values, mean and SEM are presented. Detection limit of the assay is at 80 infectious particles per lung indicated by the blue line. Homozygous Tmprss2 knock-out mice showed significantly reduced mortality compared to wild type and heterozygote mice (p<0.0001 and p = 0.0032, respectively, using the log rank test). Viral load was not significantly different in infected wild type mice compared to infected homozygous mutant mice at days 1 to 3 p.i.