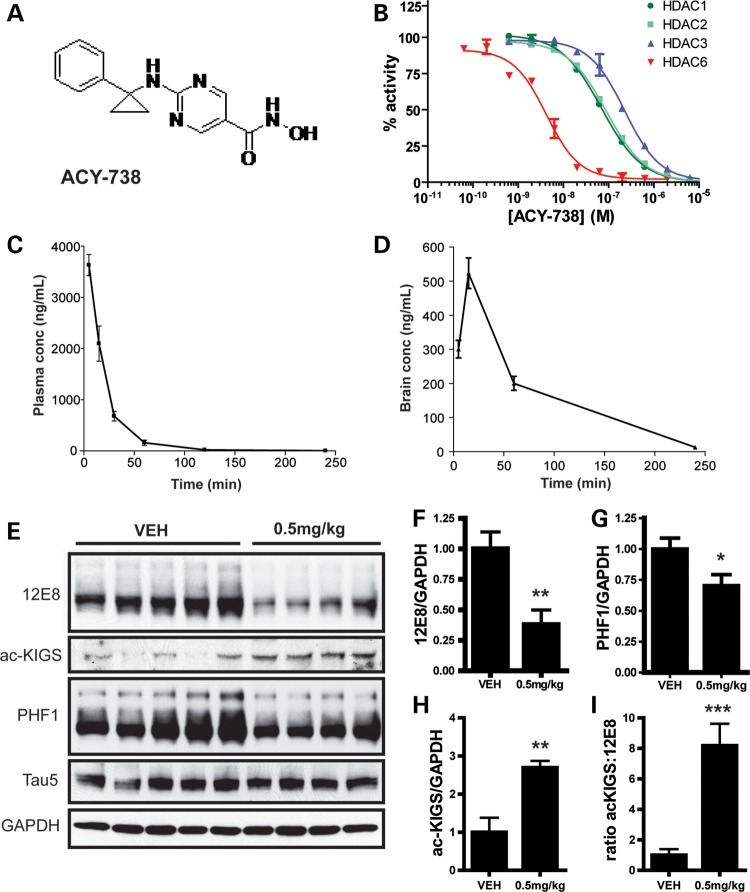
Figure 4.
Selective HDAC6 inhibition decreases p-tau levels in vivo. (A) Structure of ACY-738. (B) Specificity of ACY-738 for HDAC6 in comparison to HDAC1-3 was assessed. (C and D) Non-transgenic mice were injected with ACY-738 (10 mg/kg), and drug levels were assessed in plasma (C) and brain (D) (n = 3). (E) FVB non-transgenic mice were injected subcutaneously for 3 days with ACY-738 (0.5 mg/kg; n = 4–5 mice/group). Brains were collected 1 h after the last injection, and tau levels analyzed by immunoblotting. Blots are representative of three-independent experiments. (F) Quantitation of 12E8 immunoreactivity revealed a significant decrease in mice treated with 0.5 mg/kg ACY-738 (t = 3.3; P = 0.01). (G) Quantitation of PHF1 immunoreactivity normalized to GAPDH revealed a significant decrease in ACY-738-treated mice (t = 2.3; P = 0.05). (H) A significant increase in ac-KIGS immunoreactivity was detected in mice injected with ACY-738 (t = 3.7; P = 0.008). (I) The ratio of ac-KIGS to 12E8 is significantly elevated by ACY-738 treatment (t = 5.38; P = 0.001). All data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001.