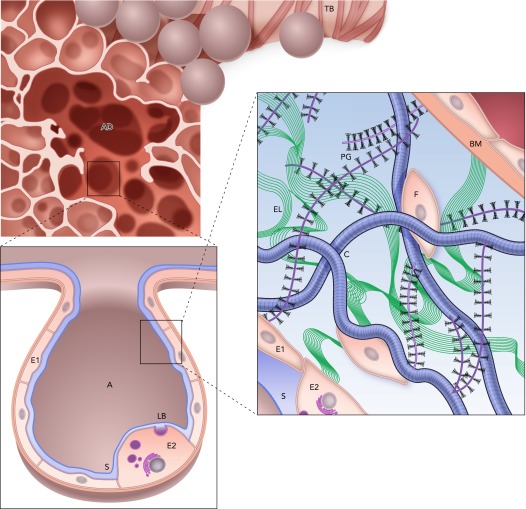
FIGURE 1.
Structure and complexity of the parenchyma at three length scales
Top: a terminal bronchiole (TB) leading to an alveolar duct (AD). Bottom left: a zoom into a single air-filled alveolus (A) with type I (E1) and type II (E2) alveolar epithelial cells covered by a thin liquid layer. The surfactant (S) molecules at the air-liquid interface. Secretion of lamellar bodies (LB) by the E2 cell is also shown. Bottom right: a schematic representation of the extracellular matrix of the alveolar septal wall with various components, including amorphous elastin (El), wavy collagen (C), complex proteoglycans (PG), basement membrane (BM), and fibroblast cells (F). Image is adapted from Ref. 48 and is used here with permission from Am J Respir Crit Care Med.