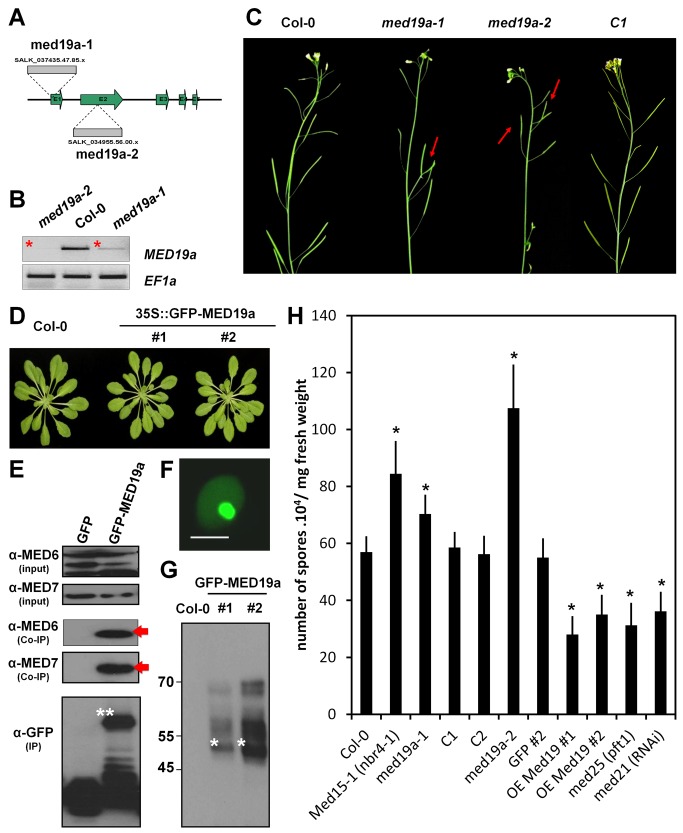
Figure 2. MED19a is a positive regulator of nuclear immunity against Hpa.
(A) Schematic diagram of T-DNA insertions in MED19a. (B) MED19a expression in med19a-1 and med19a-2 mutants. (C) Representative images of the phenotype observed in 4-wk-old floral stem of Col-0, med19a-1, med19a-2, and med19a mutant complemented line C1. (D) Developmental phenotype of Arabidopsis transgenic lines OE-MED19a compared to Col-0. (E) Immunoblot of the Co-immunoprecipitation analysis between GFP-MED19a and MED6 and MED7. Arrows point out the interaction detected between GFP-MED19a and MED6 and MED7. (F) Subcellular localisation of GFP-MED19a in Arabidopsis plant. Scale bar, 5 µm. (G) Immunoblot of proteins extracted from two independent lines expressing GFP-MED19a. Stars indicate the expected size for GFP-MED19a. Notice the upper bands in the blot that might suggest posttranscriptional modifications. (H) Monitoring of Hpa sporulation at 5 DAI in control lines (Col-0 and GFP), med19a mutant complemented lines (C1 and C2), Mediator mutants, and MED19a OE lines. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Asterisks represent the significance of individual unpaired t tests comparing the given column with the control (p value<0.01).