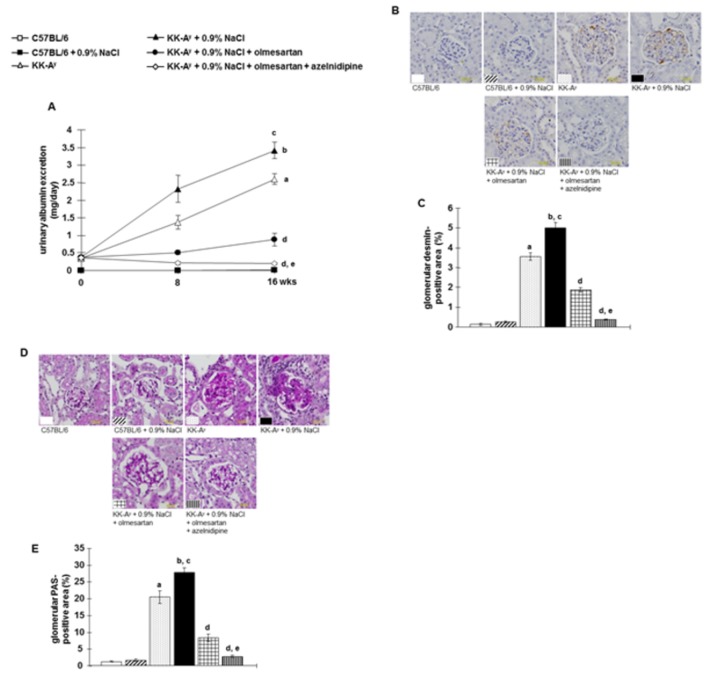
Figure 4. Albuminuria and glomerular podocyte injury.
A, KK-Ay mice showed albuminuria, which was exacerbated by further increased saline intake (n=11 in each group). B, Glomerular podocyte injury was detected by desmin immunostaining. Representative desmin-stained images (scale bar shows the values), and C, the desmin-positive area as a percentage of the total glomerular area. KK-Ay mice showed larger desmin-positive areas (brown staining) in the glomeruli, which were further increased by saline intake. Olmesartan markedly prevented these changes. However, the combination of olmesartan plus azelnidipine almost completely abrogated albuminuria and completely prevented glomerular podocyte injury. D, Glomerular sclerosis was evaluated by examining periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining. Representative micrographs of PAS-stained renal sections (scale bar shows the values), and E, the PAS-positive area within the total glomerular area. KK-Ay mice exhibit severe glomerular sclerosis, which was further exacerbated by saline intake. Olmesartan markedly prevented glomerular sclerosis. However, the combination of olmesartan plus azelnidipine exhibited greater protective efficacy against glomerular sclerosis (n=7 in each group). a P < 0.05 vs. C57BL/6, b P < 0.05 vs. C57BL/6 + 0.9% NaCl, c P < 0.05 vs. KK-Ay, d P < 0.05 vs. KK-Ay + 0.9% NaCl, e P < 0.05 vs. KK-Ay + 0.9% NaCl + olmesartan.