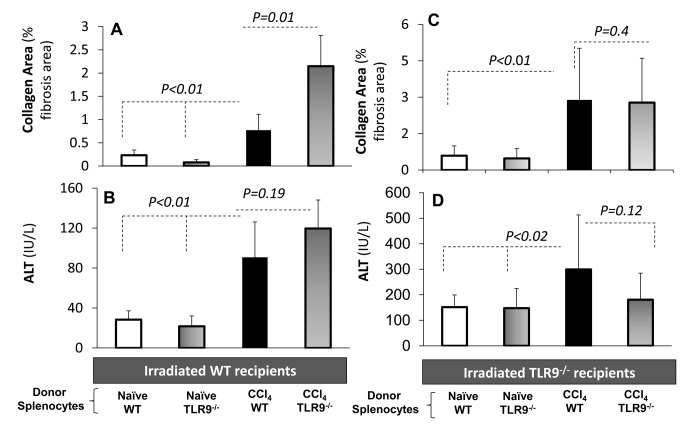
Figure 6. In vivo adoptive transfer model isolates lymphocyte outcome of each strain.
Irradiated WT or TLR9-/- recipient mice were reconstituted by naive WT or TLR9-/- donor lymphocytes, along with CCl4 fibrosis induction, as described in Materials and Methods. Accordingly, there were 4 groups of the WT recipients and another 4 groups of TLR9-/- recipients. Plain and black bars are reflecting naïve recipients reconstituted with WT or TLR9-/- donor lymphocytes, respectively. Horizontal and vertical gradient bars reflect fibrotic recipients reconstituted with WT or TLR9-/- donor lymphocytes, respectively. Recipient livers were assessed for histology collagen area, and serum ALT levels were measured. A) Collagen area significantly increased following CCl4 induction in both groups. Significant fibrosis exacerbation among WT recipients was observed when donor of lymphocytes was TLR9-/- compared to WT lymphocytes (P<0.01). B) ALT serum levels significantly increased (P<0.01) following fibrosis compared to naive recipients. TLR9-/- fibrotic recipients reconstituted with TLR9-/- or C) WT lymphocytes achieved a significant fibrosis (P<0.01) and D) serum ALT (P<0.02) progression when compared to naives. However, both fibrotic groups were similar and showed no hepatic fibrosis or serum ALT changes.