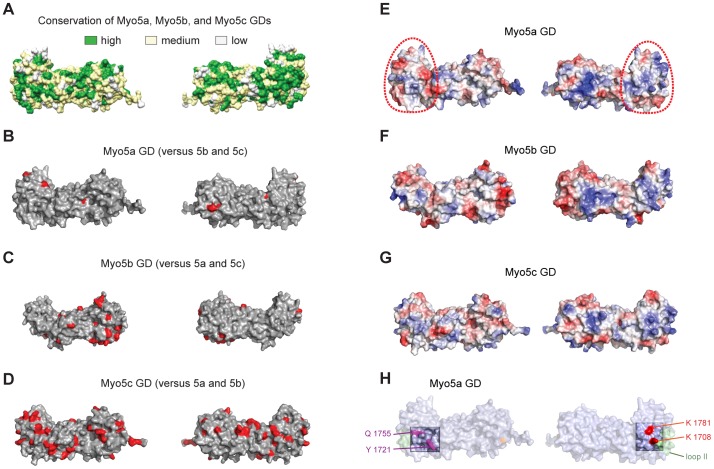
Figure 2. Analyses of surface properties of the globular domains from Myo5a, Myo5b, and Myo5c.
Orientation is as shown in Figure 1D (left) and rotated by 180° around the vertical axis (right). (A) Amino acid conservation between human Myo5a, Myo5b, and Myo5c GDs based on alignment shown in Figure S3 in File S1 and plotted on the structure of Myo5a GD. Green indicates high sequence conservation, yellow partial conservation, and white a lack of conservation. (B–D) Unique surface residues in Myo5a (B), Myo5b (C), or Myo5c (D), when compared to their respective paralogs, are shown in red. (E–G) Representation of surface potentials of Myo5a (E), Myo5b (F), and Myo5c (G). Red and blue indicate surface areas with negative and positive surface charges, respectively. White regions indicate hydrophobic regions. The surface region encircled by a red dotted line is an area with high similarity of overall surface charges amongst the three type V myosins (see also Figure S6 in File S1). This similarity might hint at a common function in all three paralogs. (H) Amino acids required for Rab11a binding are highlighted in magenta, residues in red are essential for motor autoinhibition.