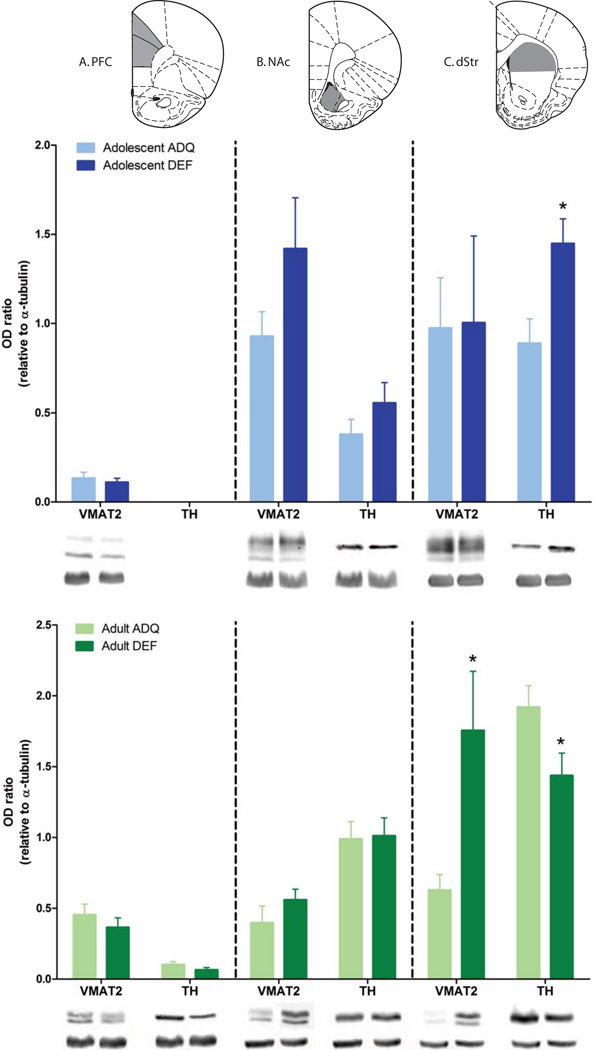
Figure 7.
N-3 PUFA generational deficiency changed markers of dopamine neurotransmission in dorsal striatum (dStr) of G2 DEF adolescent and adult rats compared to the ADQ-fed group. Protein levels of VMAT2 and TH in G2 DEF rats, adolescents or adults, were not different than those in ADQ rats in prefrontal cortex (PFC) (Panel A, top and bottom) and nucleus accumbens (NAc) (Panel B, top and bottom). In the dStr (Panel C), TH protein expression was elevated significantly in G2 DEF adolescent rats relative to the control protein, tubulin. Conversely, in the dStr of G2 DEF adult rats, protein levels of VMAT2 were elevated significantly, while TH protein expression was reduced significantly compared to ADQ-fed counterparts. Representative images are shown correspondingly below each bar graph for both the protein of interest and tubulin. Upper histology panels represent coronal rat brain atlas diagrams (66) indicating regions of interest dissected for analyses. Data are shown as mean optical density of protein of interest relative to tubulin ± SEM, n = 6–8/group, * p < 0.05 compared to age-matched respective G2 ADQ group.