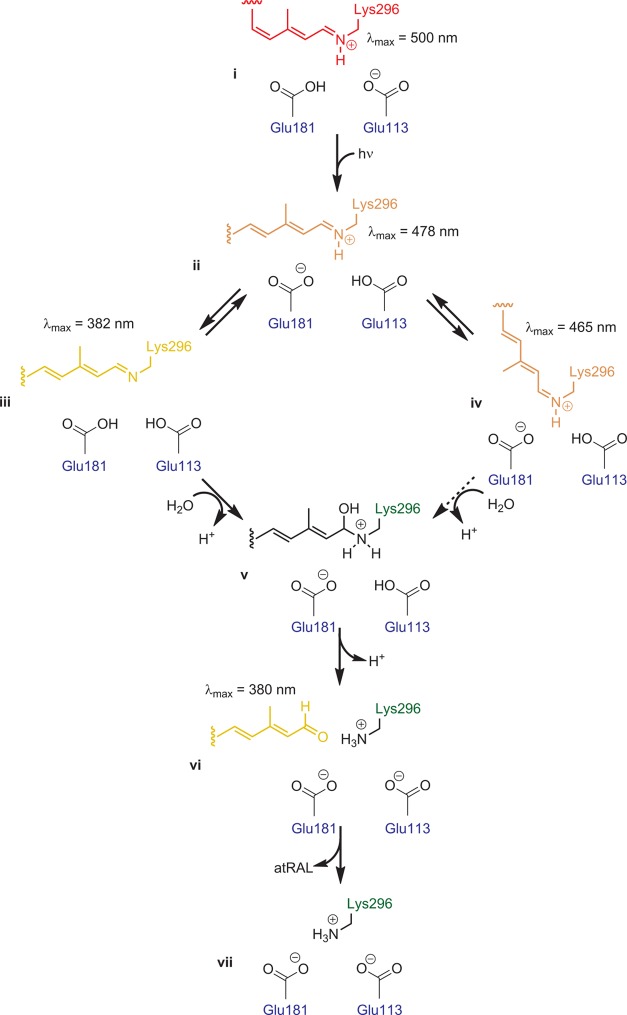
Figure 19.
Chemical changes in the rhodopsin chromophore during photoactivation. The pathway is initiated when 11-cis-retinylidene (i) absorbs a photon, leading to cis/trans isomerization. Then the Glu113 counterion of the protonated Schiff base becomes protonated, leading to the formation of Meta I rhodopsin (ii). Meta I, in turn, can convert to Meta II rhodopsin (iii), the active signaling form of rhodopsin, or, rarely, to Meta III rhodopsin (iv), a non-signaling form of rhodopsin. Both forms decay through a carbinol ammonium intermediate (v) to form a non-covalent opsin–all-trans-retinal complex (vi), which then dissociates to yield free all-trans-retinal and opsin (vii).