Figure 2.
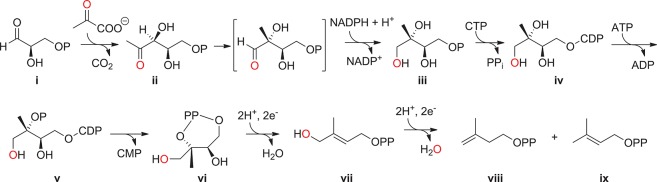
MEP (nonmevalonate) pathway for the synthesis of IPP and DMAPP. First, d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (i) is condensed with pyruvate to form 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate (DOXP, ii) catalyzed by 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (DXS) using a thiamine diphosphate cofactor with the loss of CO2. ii is isomerized and reduced by DOXP-isomeroreductase (IspC) in an NADPH-dependent manner to form 2C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate, which is then conjugated with CTP to form 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl d-erythritol (iv) in a reaction catalyzed by 2C-methyl-d-erythritol cytidylyltransferase (IspD). iv is then phosphorylated to form 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol-2-phosphate (v) by 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol kinase (IspE). v is cyclized with the loss of CMP to form 2C-methyl-d-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate (vi) by 2C-methyl-d-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase (IspF). vi is then reduced with cleavage of the cyclodiphosphate moiety to form 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl diphosphate (vii) by the iron-sulfur enzyme IspG using ferrodoxin as a cofactor. Finally, vii is further reduced by a second iron–sulfur protein IspH, giving a mixture of IPP (viii) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP, ix). The red colored oxygen atom is intended to assist in tracking of the chemical origin of the carbon skeleton. P, phosphoryl group; PPi, inorganic pyrophosphate.
