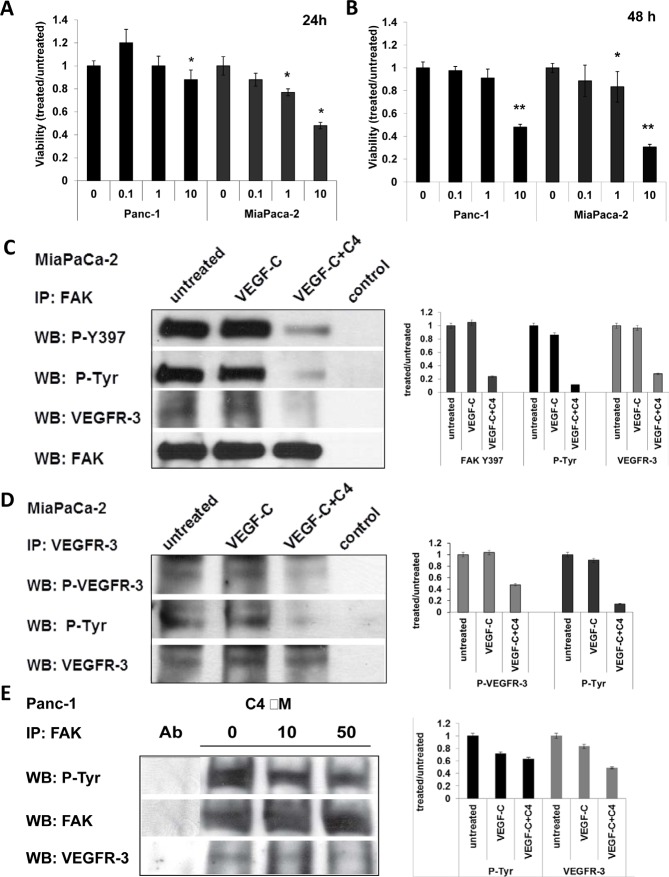
Figure 1. Compound C4 caused dose- and time-dependent decrease of viability of pancreatic cancer cells, dephosphorylation of FAK and VEGFR-3, and decrease of their complex formation.
A, B. Compound C4 caused decrease of viability of pancreatic cancer cells (MTS assay). Cells plated on 96 well plates, grown 24 h and treated 24 h (A) and 48 h (B) with selected concentrations of small molecule C4. Data of MTS assay presented as ratio of OD treated to untreated cells, 1 corresponds to the 100% viability of the untreated cells. C. C4 dose-dependent dephosphorylation of FAK and VEGFR-3 is accompanied by decrease of FAK-VEGFR-3 association in PDA cells. Cells were treated with 10 μM (MiaPaCa-2) or 10 μM and 50 μM (Panc-1) of C4 for 24 h and phosphorylation of VEGFR-3 and FAK was analyzed by immunoprecipitation (IP) with consequent western blotting (WB) with pan-phospho-tyrosine antibody 4G10, P-VEGFR-3 (Tyr 1230/1231) specific antibody and antibody to major autophosphorylation site of FAK Y397. Control IP was done with isotype of the primary antibody. FAK precipitates were analyzed for the presence of VEGFR-3 protein with VEGFR-3 specific antibody. Densitometry was performed for each IP experiment and data are presented as graphs on the right panel of each figure.