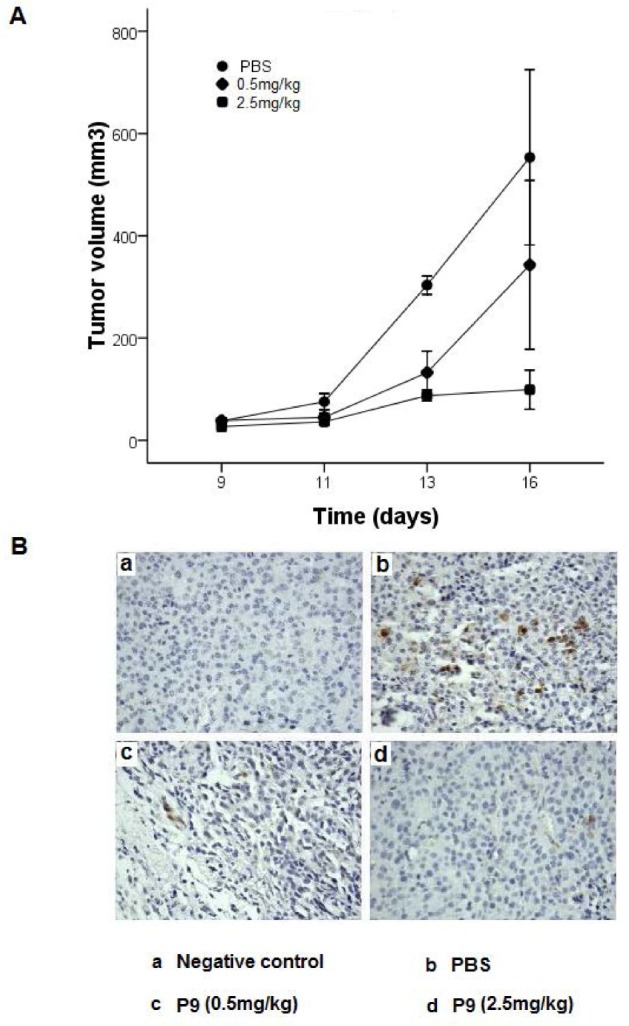
Figure 8. Synthetic P9 peptides inhibit the growth of the murine melanoma B16-F10 cells in mice.
(A) B16-F10 cells were injected subcutaneously into female C57BL/6 mice. When tumors were visible on all mice on day 7, treated mice were intraperitoneally injected with P9 on alternate days at 0.5, or 2.5 mg/kg, whereas control mice were injected with PBS (n=10 mice for each group). (B) P9 inhibits Erk1/Erk2 activation in tumors in vivo. On the next day after last injection, the B16-F10 tumors were extracted, fixed, and embedded in paraffin. Tissue sections were immunostaining for phospho-Erk1/2 as described in the Material and Methods. Meanwhile, negative control was incubated with PBS instead of monoclonal anti-phospho-Erk1/2. Negative control (Panel a), PBS (Panel b), 0.5 mg/kg (Panel c), and 2.5 mg/kg (Panel d). Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.