Figure 4.
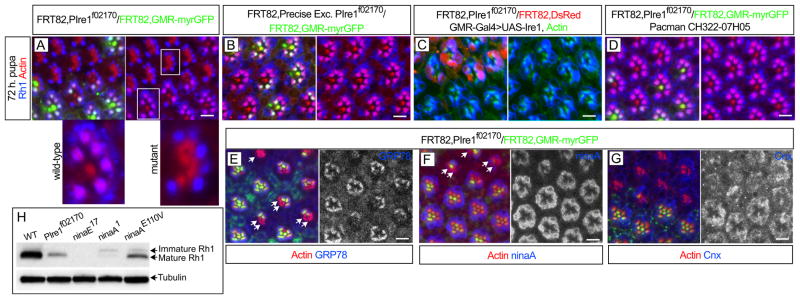
Ire1 is required for Rh1 delivery into the rhabdomere. (A) 72 h pupal eye with eyeless-Flipase induced clones of PBac{WH}Ire1f02170 homozygous cells, labeled by the absence of myrGFP (green), show defective delivery of Rh1 (blue) into the rhabdomeres (actin, red). The magnified mutant and control ommatidia are indicated with white squares. (B) Rh1 (blue) delivery into the rhabdomeres is normal in clones of a precise excision of PBac{WH}Ire1f02170 (labeled by the absence of myrGFP, green). (C) GMR-Gal4>UAS-Ire1 expression rescues Rh1 (blue) delivery into the rhabdomeres of PBac{WH}Ire1f02170 homozygous cells (labeled by the absence of DsRed). (D) The CH322-07H05 genomic construct rescues Rh1 (blue) delivery into the rhabdomeres of PBac{WH}Ire1f02170 homozygous cells (absence of myrGFP, green). (E–G) PBac{WH}Ire1f02170 homozygous cells (absence of myrGFP, green) have reduced levels (arrows) of (E) BiP/GRP78 (blue and monochrome) and (F) ninaA (blue and monochrome), but not (G) Cnx (blue and monochrome). (H) Western blot analysis of Rh1 mature (34 kDa) and immature (40 kDa) forms from adult head protein extracts of yw (WT, positive control), FRT82BPBac{WH}Ire1f02170/FRT82BCL,GMR-hid (whole eye is composed of homozygous Ire1 mutant cells as in (Stowers and Schwarz, 1999)), ninaE17 (Rh1 protein null) and 2 ninaA mutations (ninaA1=ninaAP228 and ninaAE110V). Tubulin is used as loading control. Scale bars, 10 μm.
