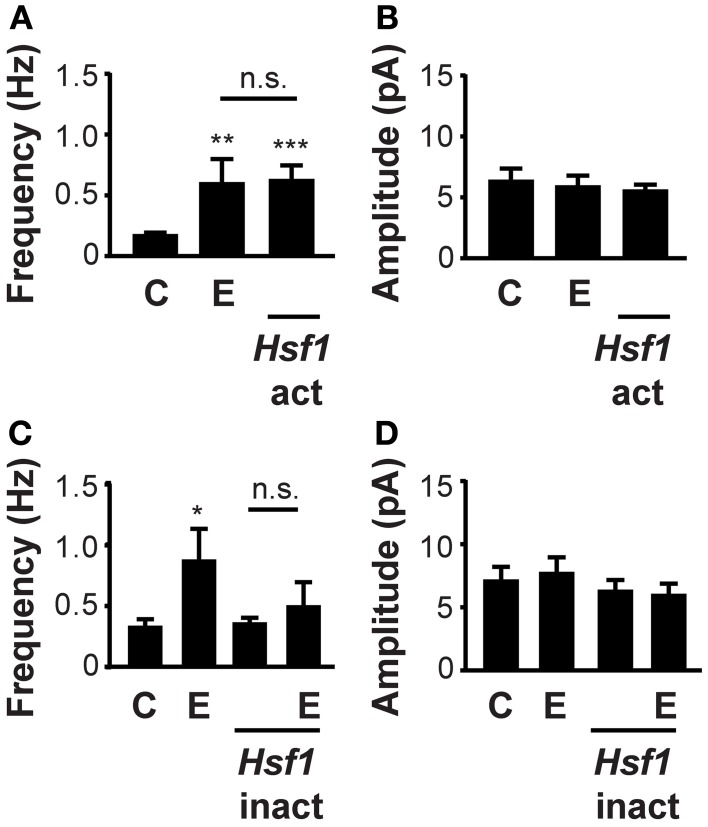
Figure 4.
Increased GABA release after ethanol exposure requires HSF1 transcriptional activity. (A) HSF1 transcriptional activity increases the probability of GABA release. Hsf1-act transfection increased mIPSC frequency, similar to the level seen with 60 mM ethanol exposure for 4–8 h (E). Control cultures were sham transfected with an empty pcDNA3.1+ construct [C; nC = 15, nE = 17, nHsf1act = 19; F(2, 48) = 3.46; p < 0.05]. (B) HSF1 activity does not alter the mean mIPSC amplitude in neurons transfected with an Hsf1-act construct, exposed to ethanol (E) or control sham transfected [C; nC = 15, nE = 17, nHsf1act = 19; F(2, 48) = 0.32; p = 0.73]. (C) Ethanol stimulation of mIPSC frequency is mediated by activated HSF1. Hsf1-inact transfection reduced the effects of ethanol (E) on mIPSC frequency. Hsf1-inact transfection alone had no effect on mIPSC frequency compared to control cultures sham transfected with empty pcDNA3.1+ construct [C; nC = 16, nE = 10, nHsf1inact = 12, nHsf1inact+E = 14; F(3, 48) = 2.56; p = 0.07]. (D) HSF1 activity does not alter the mean amplitude of mIPSCs in neurons transfected with an Hsf1-inact construct, exposed to ethanol (E) or vehicle control [C; nC = 16, nE = 10, nHsf1inact = 12, nHsf1inact+E = 14; F(3, 48) = 0.0639; p = 0.60; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, or n.s. denotes no significance].