Figure 7.
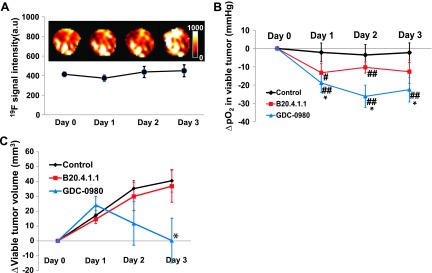
(A) PFCs remained in the tumor throughout the course of the 4-day study following i.v. delivery. No significant loss of 19F signal was observed, which enabled a multiday longitudinal study of pO2 change. Every effort was made to locate the same imaging slice in the tumor according to the distance and shape, but deviations may still exist due to the positioning of the animal on different days, as well as tumor growth. (B) The temporal evaluation of mean ΔpO2 in viable tumor. Both the B20.4.1.1 and GDC-0980 groups exhibited a decrease in pO2 in the viable tumor posttreatment relative to pretreatment levels. When compared with the control group, the GDC-0980 group exhibited a significant decrease in viable tumor pO2, whereas the B20.4.1.1 group showed a trend toward a reduction of pO2 (P = .14 on day 1). (C) The viable tumor volume change with time. Only the GDC-0980 group showed a significant reduction on day 3 in comparison with the control. *P < .05 in comparison with the control group. #P < .05 versus pretreatment; ##P < .01 versus pretreatment. Data are shown as means ± SEM.
