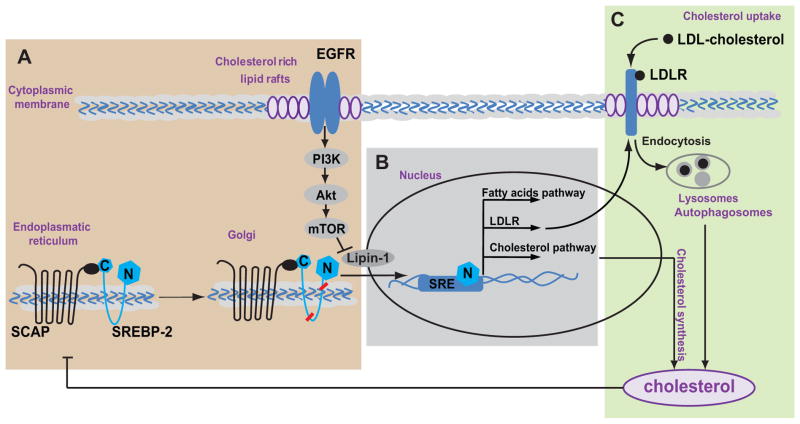
Figure 1. Cholesterol homeostasis regulation.
A. Activated EGFR and mTOR signaling promotes SREBP-SCAP complex to move to the Golgi where it undergoes cleavage to form an active nuclear SREBP fragment (N, blue diamonds). B. In the nucleus, the nuclear fragment of SREBP (N, blue diamonds) binds to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequences (56) and induces expression of fatty acid and cholesterol pathway genes and the LDL receptor (LDLR). C. Uptake of exogenous LDL cholesterol is via its binding to LDL receptor. LDLR internalization and degradation in lysosomes and autophagosomes releases free cholesterol (34). Under the conditions of excess, cholesterol acts as a negative regulator by binding to SCAP and blocking SREBP processing.