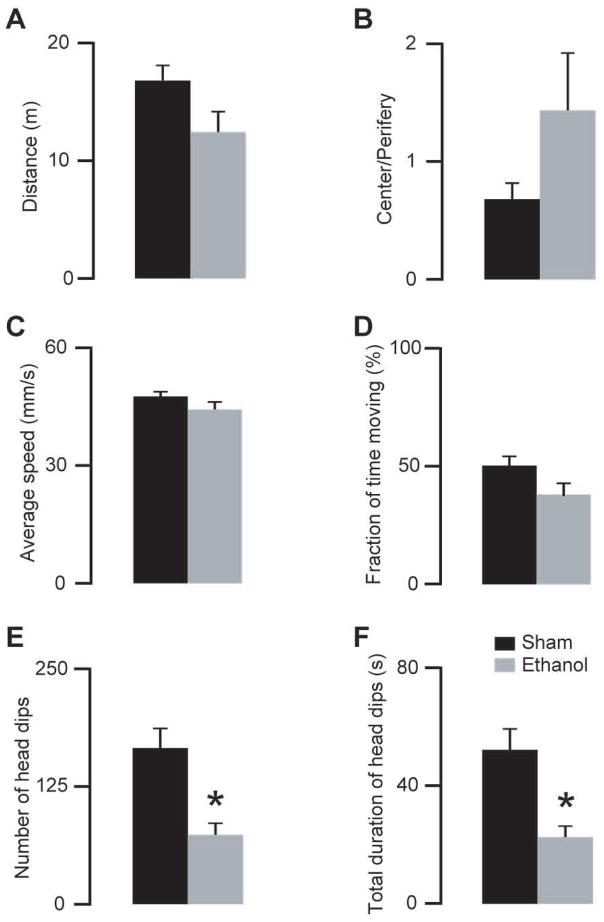
Figure 4.
Effects of a moderate dose of ethanol (1.6 g/kg i.p.) on locomotor and exploratory activities. A–D) Ethanol (grey bars) did not change the locomotor activity of the mice compared with saline injected (black bars) mice (unpaired two-tailed t-test, p>0.07 for all comparisons). E–F) Ethanol treated animals showed less head dips (unpaired two-tailed t-test, p=0.003) and decreased duration of the total head dips (unpaired two-tailed t-test, p=0.004) (*indicate statistically significant differences p<0.05; n=8 ethanol, n=8 saline injected mice, same animals as on Fig 3).