Figure 3. From user input to system output the platform engine controls the execution of workflows as follows:
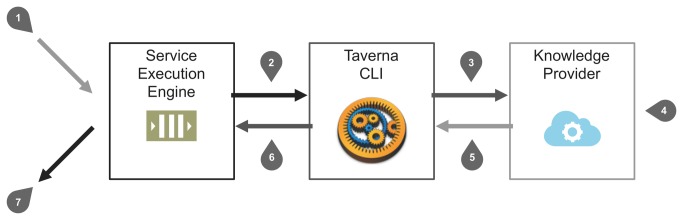
1) One or more knowledge provider algorithms are selected to evaluate researcher-submitted datasets. The platform engine sends the request to the service execution engine. 2) An XML file with the input data (obeying the platform’s interoperability standard) is generated and its path provided to the service execution engine, along with the path for the workflows associated with each knowledge provider algorithm. The workflow execution is then triggered by a system call. 3) The Taverna command line tool loads the knowledge provider’s workflow, starting the processing tasks. 4) The knowledge provider execution proceeds internally, executing the miscellaneous workflow tasks. 5) The workflow delivers an XML data file (obeying the platform’s interoperability standard) with the algorithm output. 6) The service execution engine loads the XML output file and transfers the results to the platform engine. 7) The engine stores the data in the knowledge base and makes it promptly available for delivery in the web workspace.
