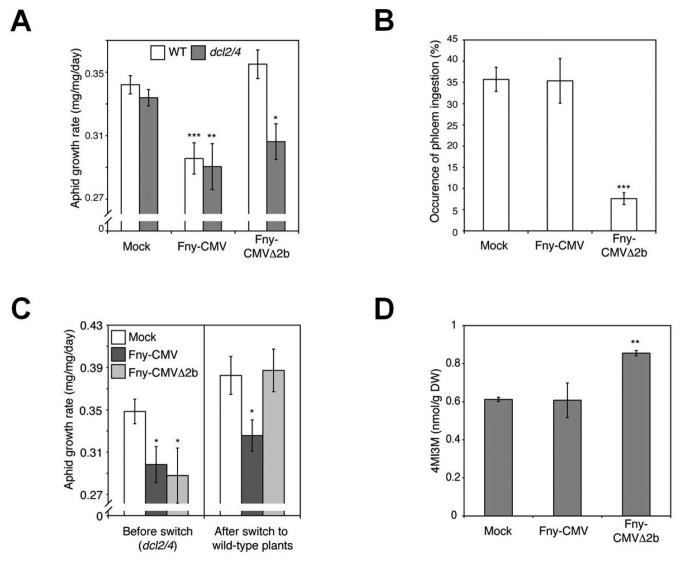
Figure 9. The CMV 2a protein triggers feeding deterrence in CMV-infected Arabidopsis plants.
(A) Growth rate of individual aphids placed on dcl2/4 plants infected with Fny-CMV or Fny-CMVΔ2b, n≥24. (B) Electrical penetration graph analysis of the percentage occurrence of phloem ingestion over 12-hour periods for aphids feeding on dcl2/4 mutants infected with Fny-CMV or Fny-CMVΔ2b, n=15. (C) Results of host-switching experiments reporting the growth rate of aphids moved from mock-inoculated or virus-infected dcl2/4 plants (“before switch”) to untouched wild-type plants (“after switch”), n≥24. (D) Accumulation of the aphid feeding deterrent, 4-methoxy-indol3yl-methyl-glucosinolate (4MI3M) in virus-infected dcl2/4 mutants, measured by high performance liquid chromatography, n=3. Asterisks indicate results of Student’s t-tests compared to the mock-inoculated plant of each genotype: *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.