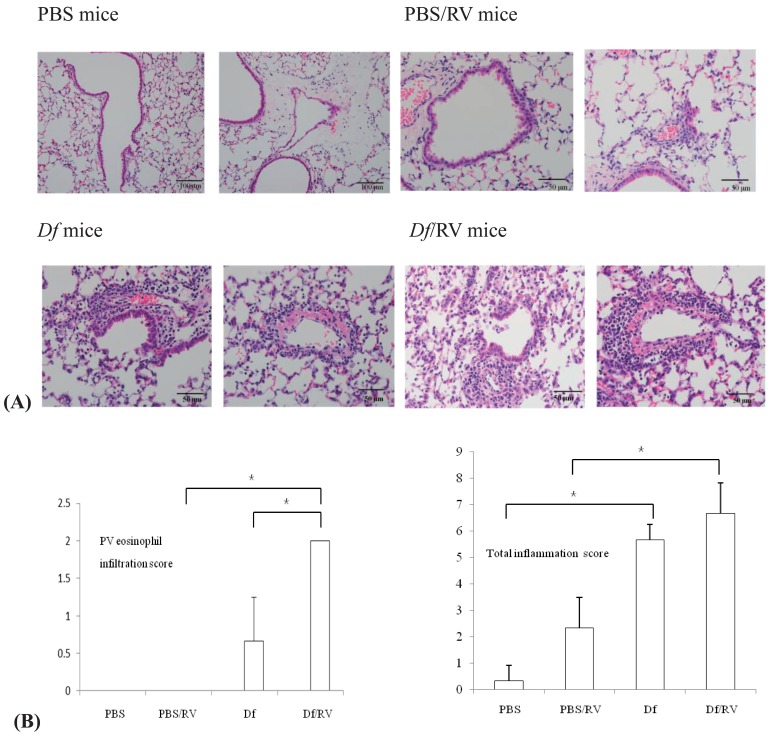
Fig. 4.
(A) Hematoxylin and eosin-stained lung sections (n=3 mice per group). Rhinovirus (RV) infection induced focal loss of bronchial epithelial cells (left) and an increase in perivascular inflammatory cell infiltration (right) in Dermatophagoides farinae (Df) sensitized and challenged mice (Df mice). Perivascular eosinophil infiltration was observed in Df mice and in Df mice with RV infection (Df/RV mice) (×100, scale bars indicate 100 µm for phosphate buffered saline-treated mice [PBS mice]; ×200, scale bars indicate 50 µm for the other 3 groups). (B) Perivascular (PV) eosinophil infiltration and total inflammation score (n=3 mice per group). PBS mice, phosphate buffered saline-treated mice; Df mice, Dermatophagoides farinae sensitized and challenged mice; RV, rhinovirus. *P<0.05.