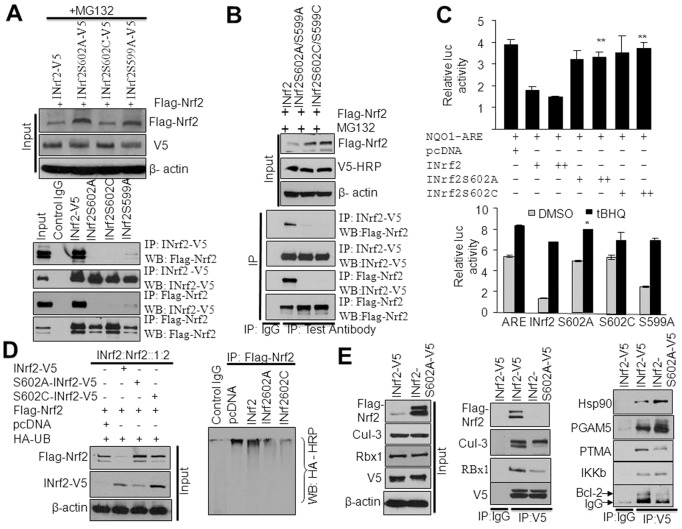
Fig. 3.
INrf2S602 phosphorylation is required for the interaction of INrf2 with Nrf2. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected with FLAG-Nrf2 and INrf2 or serine mutant INrf2 plasmids and treated with MG132 (8 hours). The interaction of FLAG-Nrf2 with INrf2-V5 mutant INrf2S602A-V5, INrf2S602C-V5 and INrf2S599A-V5 was analyzed by reciprocal immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. (B) HepG2 cells were co-transfected with FLAG-Nrf2, wild-type INrf2 or double-mutant INrf2 plasmids and treated with MG132. The interaction of FLAG-Nrf2 with INrf2-V5 and double mutants of INrf2 was analyzed by reciprocal immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. (C) Luciferase assay. HepG2 cells were co-transfected with NQO1 ARE-Luc, Renilla and INrf2 or INrf2S602A or INrf2S602C and relative luciferase activity was measured (top panel). Similarly, HepG2 cells were co-transfected with NQO1 ARE-Luc and INrf2V5 or various mutant INrf2 constructs, treated with DMSO or 50 µM tBHQ and relative luciferase activity was measured (bottom panels). The data shown are means ± s.d. of three independent transfection experiments. (D) Nrf2 ubiquitylation. HepG2 cells were co-transfected with INrf2 and mutant INrf2 with FLAG-Nrf2 and HA-Ub constructs and FLAG-Nrf2 levels and Nrf2 ubiquitylation were analyzed (left and right panels). (E) HepG2 cells were co-transfected with INrf2-V5 or INrf2S602A mutant plasmid with FLAG-Nrf2 and interaction of INrf2 and mutant INrf2 with Nrf2 and INrf2 known interacting partners (proteins) were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting.