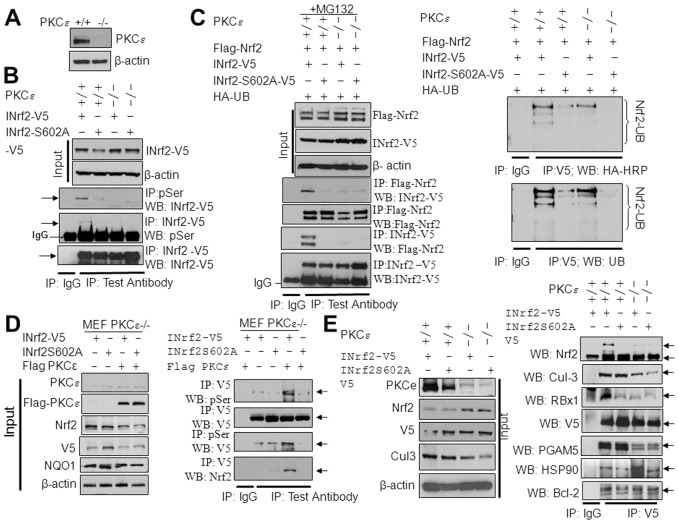
Fig. 4.
PKCε-mediated phosphorylation of INrf2S602, INrf2−Nrf2 interaction and Nrf2 degradation in PKCε+/+ and PKC−/− MEFs. (A) Immunoblot analysis of PKCε levels in PKCε+/+ and PKCε−/− MEFs. (B) INrf2 serine phosphorylation analysis. INrf2-V5 and mutant INrf2S602A-V5 plasmids were transfected into PKCε+/+ and PKCε−/− MEFs and INrf2 serine phosphorylation was analyzed by reciprocal immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. (C) Interaction of INrf2-V5 and mutant INrf2S602A-V5 with FLAG-Nrf2 was analyzed in the PKCε+/+ and PKCε−/− MEFs after transfection of indicated plasmids by reciprocal immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting using specific antibodies (left panels). Nrf2 ubiquitylation was analyzed from PKCε+/+ and PKCε−/− cells transfected with INrf2 and mutant INrf2S602A as indicated (right panels). (D) PKCε−/− MEFs were co-transfected with INrf2-V5 or mutant INrf2S602A-V5 plasmids with pcDNA or FLAG-PKCε and INrf2 serine phosphorylation and interaction with Nrf2 was analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting using specific antibodies. (E) PKCε+/+ and PKCε−/− cells were transfected with INrf2-V5 and mutant INrf2S602A-V5 plasmids and interaction of INrf2 and mutant INrf2 with Nrf2 and INrf2 known interacting partners was analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting.