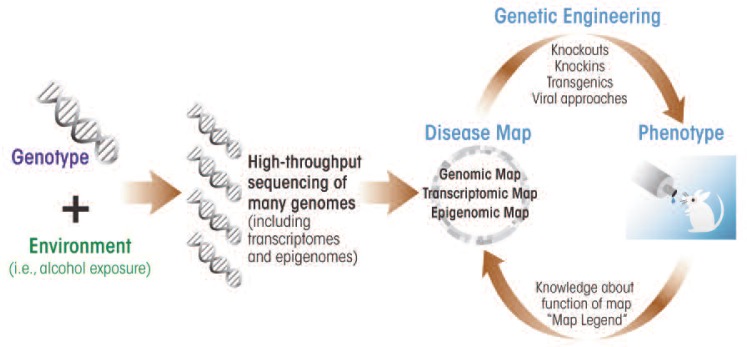
Figure.
Exploring the relationship between genotype and phenotype by using high-throughput sequencing and genetically engineered animal models. Novel high-throughput “next-generation sequencing” technology can be used together with new genetic engineering technology to understand gene function in alcoholism. Compared with traditional sequencing, “next-generation sequencing” allows researchers to efficiently and cost-effectively obtain large amounts of genomic data (e.g., from large cohorts of humans with and without disease) to detect all the genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic variation associated with the disease, creating comprehensive “disease maps.” In a next step, functional information can be attached to these disease maps that defines how the various components of the map (i.e., individual genes) act and interact, for example, using genetically engineered animal models. Genomic variations associated with human diseases can be engineered into rodent models (or other experimental organisms) and detailed phenotypic analyses can be performed, further refining disease maps with functional annotation.