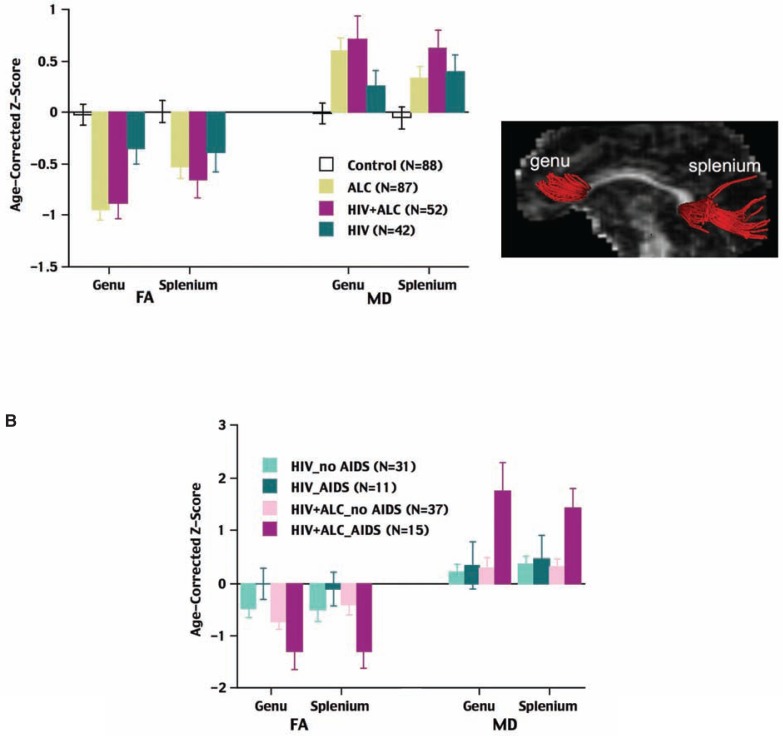
Figure 3.
Example of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) fiber tracking of the frontal (i.e., genu) and posterior (i.e., splenium) regions of the corpus callosum displayed in red. A) Representation of the differences in two DTI measures in patients with alcoholism alone, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection alone, HIV and alcoholism, and control subjects with neither condition. Fractional anisotropy (FA)* and mean diffusivity (MD) are measures reflecting the integrity of a white matter fiber; lower scores for FA and higher scores for MD indicate fiber integrity compromise. All three patient groups had lower callosal FA and higher MD than the control subjects, but the genu abnormalities of the two alcohol groups were statistically significant. B) FA and MD values in the HIV-infected patient groups divided according to their history of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV-infected patients with AIDS and alcoholism showed the greatest callosal abnormalities.