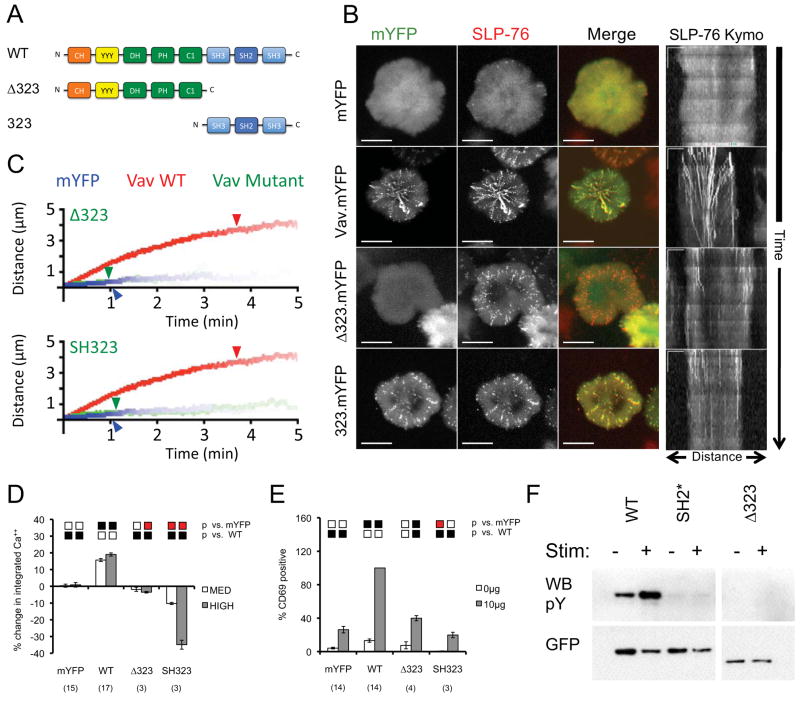
Figure 3. The C-terminal homology domains of Vav1 are necessary and sufficient for microcluster entry, but are insufficient for microcluster movement and Vav1-dependent signaling.
(A) The domain structure of Vav mutants used in this figure. (B) JV.SC cells transiently transfected with the indicated Vav1.mYFP constructs were stimulated and imaged as in Figure 2B. Representative maximum-over-time projections (left) and kymographs (right) were selected from 3 independent experiments. Scale bars as in Figure 2B. (C) Composite kymographs depicting SLP-76 MC movement and persistence were prepared as in Figure 2C. Arrowheads correspond to the half-life of SLP-76 MC for each condition. See Table 1 for further analysis. (D) TCR-induced CD69 expression was determined in J.Vav1 cells reconstituted with the indicated Vav1.mYFP chimeras. Presentation and statistics are as in Figure 2E. (E) TCR-induced intracellular calcium responses were measured in J.Vav1 cells reconstituted with the indicated Vav1.mYFP chimeras. Presentation and statistics are as in Figure 2D. (F) The indicated Vav1.mYFP chimeras were expressed in Jurkat E6.1 cells and immunoprecipitated from unstimulated and TCR-stimulated lysates using GFP-specific antibodies. Membranes were sequentially western blotted for phosphotyrosine and GFP. Images are representative of 3 independent experiments.