Figure 1. Schematic representation of the BR feedback system.
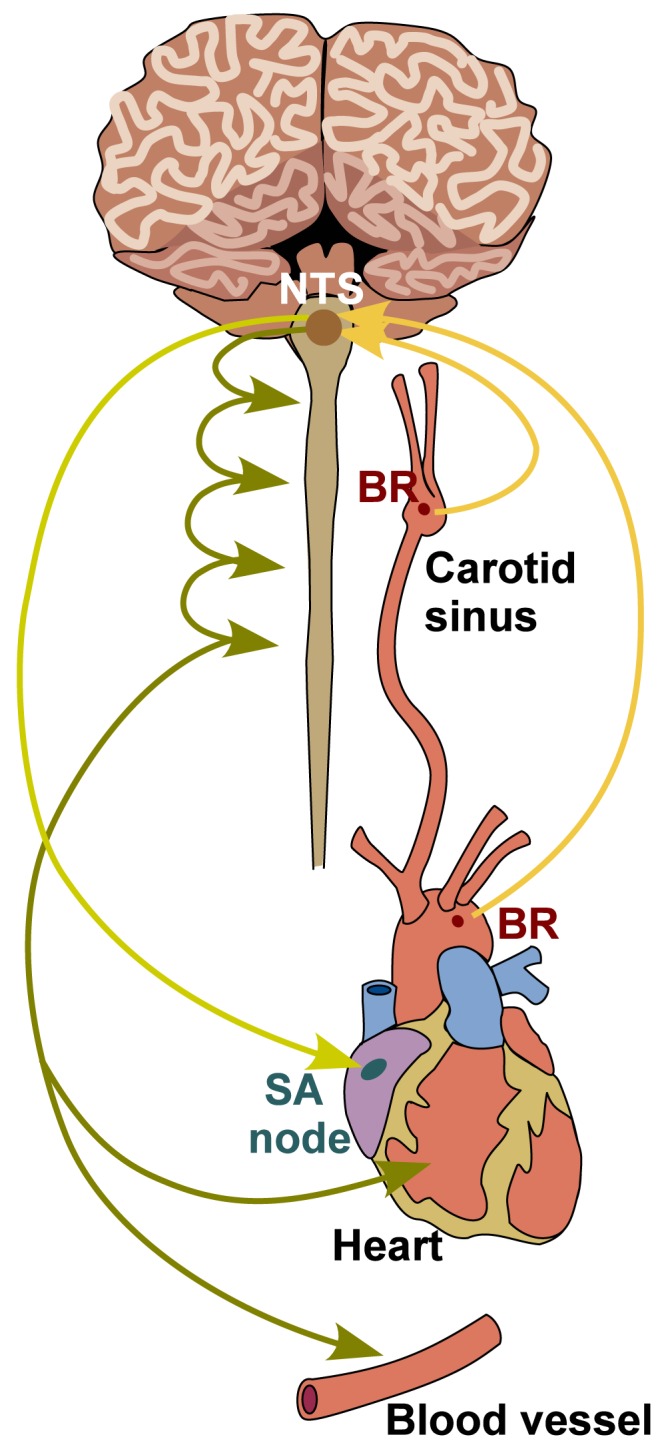
Stretch sensitive BR neurons originate in the carotid sinuses and the aortic arch. In these arteries, dynamic changes in blood pressure cause vessel deformation, modulating stretch of mechanoreceptors channels found in the BR nerve endings. Stimulation of these receptors modulates frequency of action potential formation, a signal integrated in the NTS. From the NTS, efferent sympathetic and parasympathetic outputs are generated determining the concentrations of neurotransmitters acetylcholine and noradrenaline, which stimulate or inhibit heart rate, cardiac contractility, vascular resistance and compliance, the latter via activation of smooth muscle cells constricting or dilating the radius of arteriolar vessels.
