Table 5. Optimized nonlinear models of BR response: wall strain models.
| kwall | A 0 | Am | α | k | α 1 | α 2 | β 1 | β 2 | s 1 | s 2 | τa | τb | p 1 | p 2 | R 2 | RMSE | |
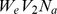 IC IC |
0.0063 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 2 | 480 | 100 | 6.46 | 46.75 | ||||||||
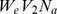 opt opt |
0.0063 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 2 | 1105 | 346 | 6.44 | 46.89 | 0.950 | 2.507 | ||||||
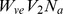 IC IC |
0.0063 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 2 | 480 | 100 | 0.030 | 0.01 | 6.46 | 46.75 | ||||||
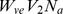 opt opt |
0.0063 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 2 | 1112 | 349 | 0.028 | 0.01 | 6.44 | 46.77 | 0.950 | 2.517 | ||||
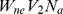 IC IC |
1 | 3 | 150 | 10 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 480 | 100 | 6.46 | 46.75 | |||||||
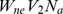 opt opt |
1 | 32.6 | 150 | 10 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 619 | 109 | 6.44 | 46.89 | 0.952 | 2.458 |
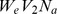 ,
, 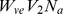 , and
, and 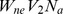 , of BR response, we present the initial and optimized values of their parameters. We used the BR firing data published by Brown [20] for a sinusoidal-like pressure profile. For the three models,
, of BR response, we present the initial and optimized values of their parameters. We used the BR firing data published by Brown [20] for a sinusoidal-like pressure profile. For the three models,
