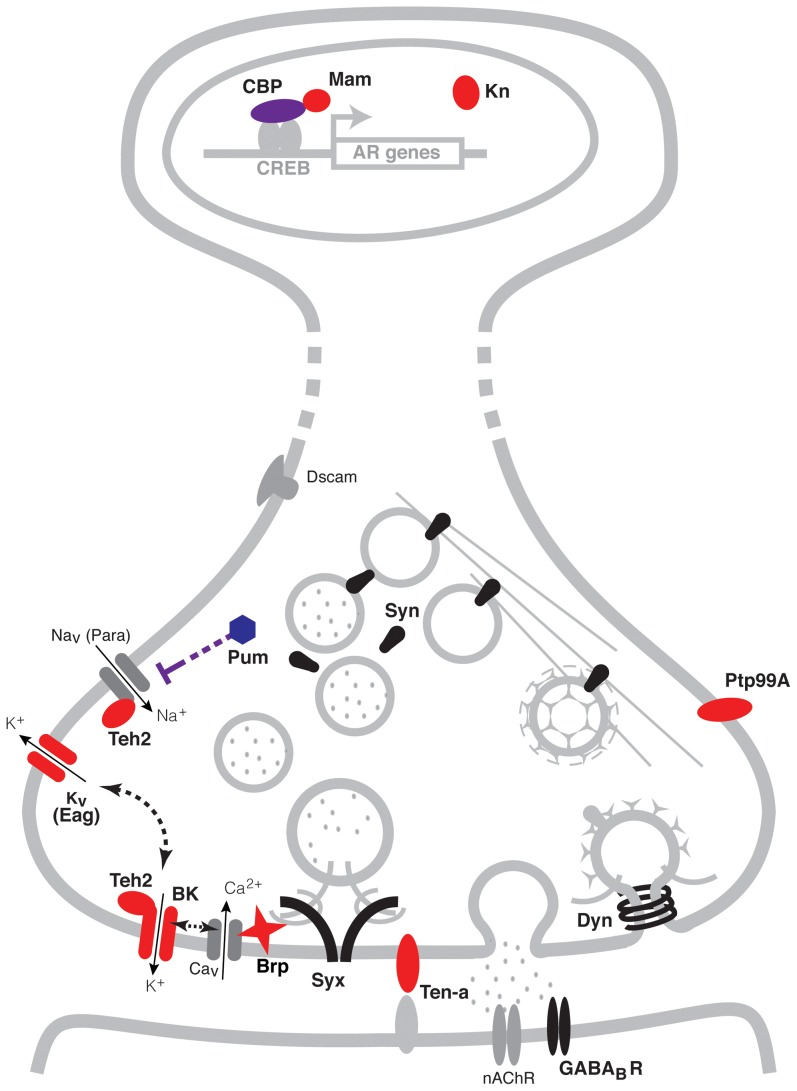
Figure 5. A pre-synaptic network model of alcohol tolerance.
Schematic representation of the cellular location of the proteins encoded by the cohort of genes identified in this study. Proteins depicted in blue belong to expression cluster #1, while those in red belong to cluster #4. Seven of the ten genes identified encode proteins that reside at the pre-synaptic terminals of neurons. Two encode ion channel proteins directly involved in the modulation of neural excitability (Eag and BK), two encode proteins that possess ion-channel regulator roles (Pum and Teh2), one encodes a pre-synaptic active zone component that provides support to transmitter release (Brp) and two encode transmembrane proteins involved in neuronal morphogenesis (Ptp99A and Ten-a). Three other genes positively identified to affect tolerance encode transcription modulator proteins. These are the CBP histone acetyl-transferase encoded by nej, the transcription co-activator Mam and the innate immune factor Kn. Other synaptic proteins previously associated with alcohol tolerance, are depicted in black. These proteins include Synapsins (Syn), Dynamin (Dyn), Syntaxin 1A (Syx) and the GABAB post-synaptic receptor (GABABR). While all these genes have known roles in specific synaptic processes, together with the genes identified here, they have the capacity to orchestrate neural adaptation in response to alcohol. Proteins and structures in gray are included to provide context.