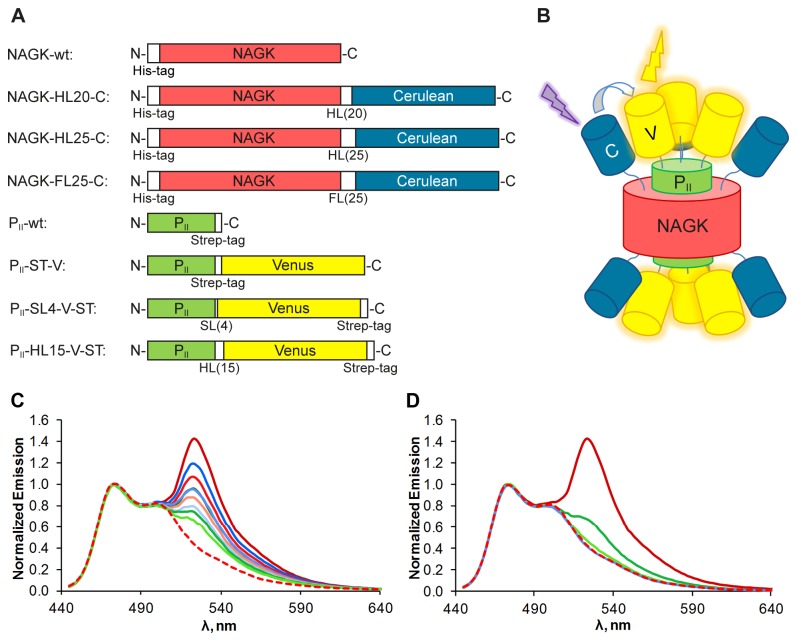
Figure 1. Fusion protein constructs and their FRET-performance.
(A) Schematic representation of NAGK and PII fusion proteins. Linker domains are denoted “HL” for helical linker, “FL” for flexible linker and “SL” for short linker with the corresponding number of amino acids in brackets. All domains are shown in the same scale. (B) Schematic representation of the assembled complex of FP-tagged PII and NAGK. Two PII trimers sandwich one NAGK hexamer. Cerulean domains are shown in blue, Venus domains are shown in yellow. (C) Emission spectra from different combinations of NAGK‑Cerulean and PII-Venus variants and NAGK‑FL25‑C alone, excited at 433 nm, emission scan from 445 to 640 nm. NAGK‑FL25‑C + PII-ST‑V in dark red, + PII-SL4‑V‑ST in red, + PII-HL15‑V‑ST in light red. NAGK‑HL20‑C + PII-ST‑V in dark blue, + PII-SL4‑V‑ST in blue, + PII-HL15‑V‑ST in light blue. NAGK‑HL25‑C + PII-ST‑V in dark green, + PII-SL4‑V‑ST in green, + PII-HL15‑V‑ST in light green and NAGK‑FL25‑C without PII in dashed red. All spectra were corrected from background Venus emission and normalized to the Cerulean peak at 475 nm for better comparability. The peaks at 525 nm represent the Venus fluorescence induced by energy transfer from Cerulean. (D) Emission spectra from NAGK‑FL25‑C + PII-ST‑V in dark red, + PII-S49G‑ST‑V in green, + PII-E85A‑ST‑V in light green, + PII-S49G‑E85A‑ST‑V in blue and NAGK‑FL25‑C without PII in dashed red. Note that the corrected spectrum recorded with the double mutant PII-S49G‑E85A‑ST‑V is identical to the spectrum of NAGK‑FL25‑C in the absence of PII.