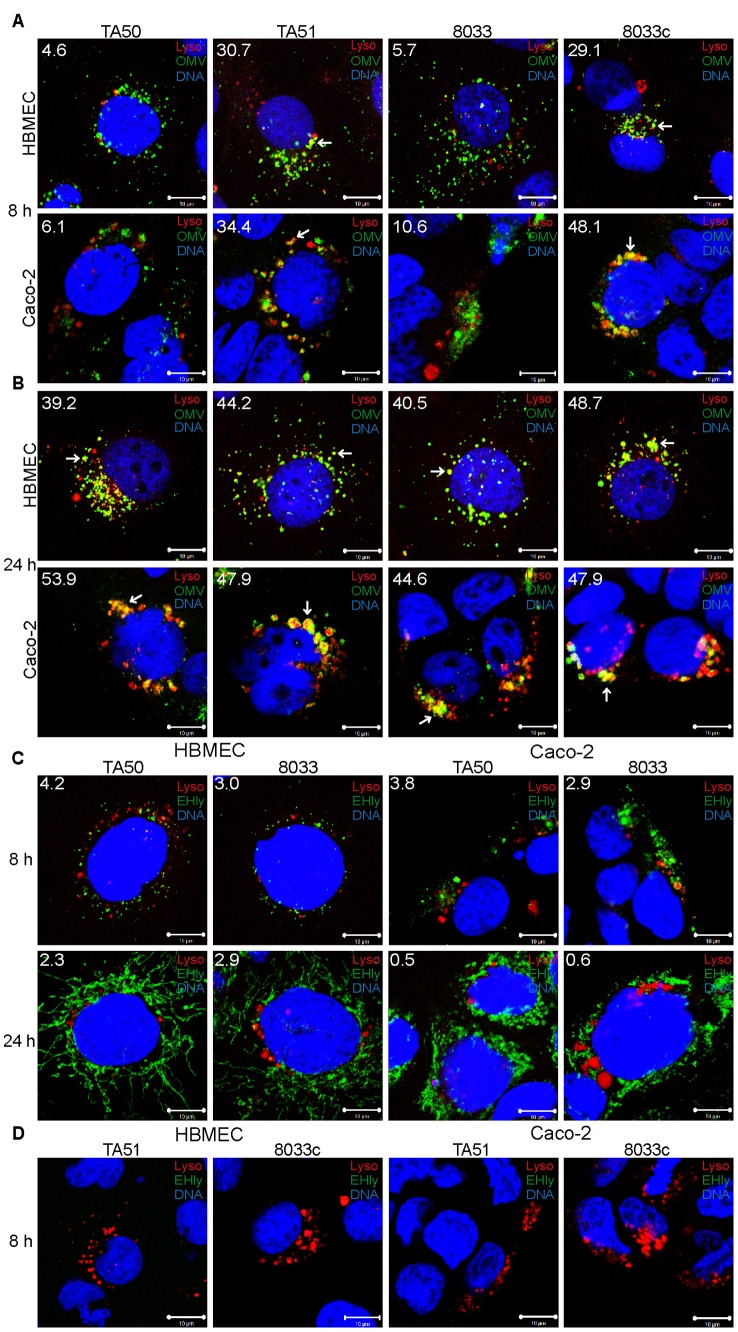
Figure 10. Releasing of EHEC-Hly from lysosomes leads to a transient loss of lysosomal function.
(A, B) HBMEC and Caco-2 cells were incubated with EHEC-Hly-containing (TA50 or 8033) or EHEC-Hly-free (TA51 or 8033c) OMVs for 8 h (A) and 24 h (B). OMVs were stained with rabbit anti-E. coli LPS antibody and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (green), lysosomes with Lysotracker Red DND-99 (red) and nuclei with DRAQ5 (blue). (C, D) HBMEC and Caco-2 cells were incubated with TA50 or 8033 OMVs (C) or with TA51 or 8033c OMVs (D) for 8 h and 24 h. EHEC-Hly (EHly) was stained with rabbit anti-EHEC-Hly antibody and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (green), lysosomes with Lysotracker Red DND-99 (red), and nuclei with DRAQ5 (blue). Pictures were taken and processed as described in the legend to Figure 4. Colocalized red and green signals appear in yellow (examples in panels A and B are depicted by arrows). White numbers indicate the percentages of OMVs or EHEC-Hly colocalized with Lysotracker Red DND-99-positive lysosomes (averages from at least five different samples) calculated using the BioImageXD6 colocalization tool. Scale bars are 10 µm. The pictures shown in panel D (8 h of incubation) are also representative of 24 h (no EHEC-Hly was detected in cells treated with EHEC-Hly-free OMVs at any of these time points).