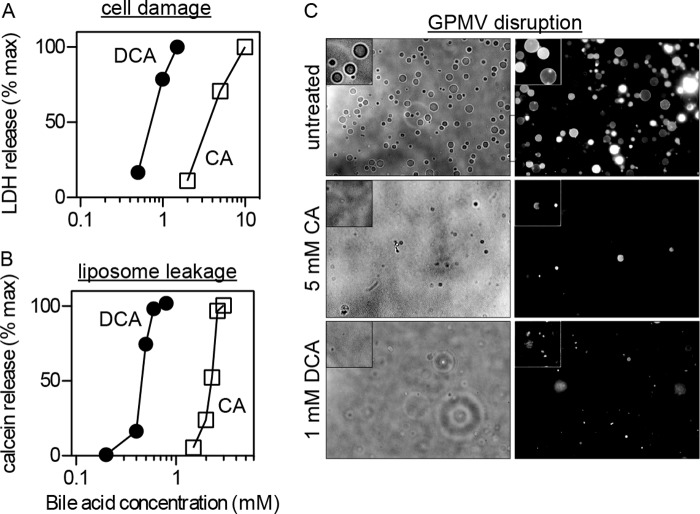
FIGURE 1.
Bile acid-induced cell injury correlates with plasma membrane vesicle dissolution. A, cell toxicity quantified by leakage of the cytoplasmic enzyme LDH is sensitive to millimolar cholic and deoxycholic acid treatment. B, synthetic liposome leakage, measured by release of calcein, correlates with cytotoxicity. C, phase contrast imaging (at room temperature) of isolated GPMVs shows that treatment of GPMVs with 1 mm DCA or 5 mm CA leads to near-complete dissolution of membranes. Higher BA concentrations lead to no observable vesicles (insets show magnifications of representative areas). The quantitative agreement between these results strongly suggests a mechanistic link between membrane disruption and cytotoxicity. All results are representative of at least three independent experiments.