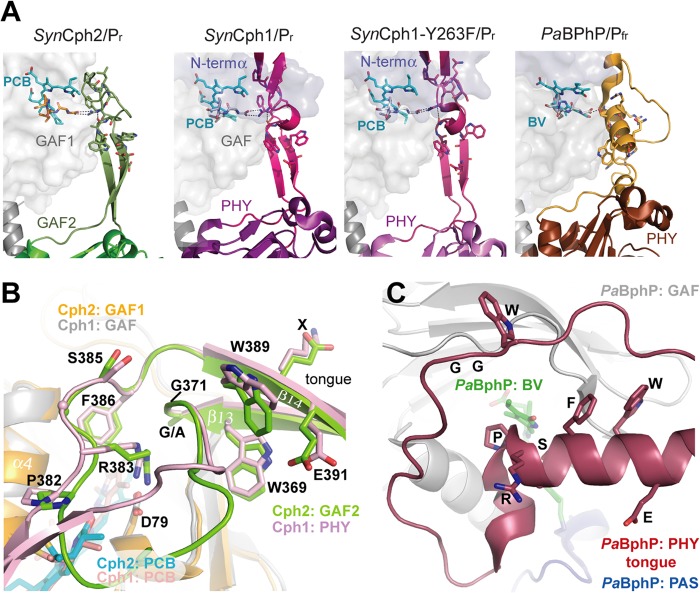
FIGURE 7.
The tongue-like region of SynCph2(1–2). A, structure and interactions between the tongues and the chromophore-bearing GAF domains of phytochromes. B, comparison of the tongue regions of SynCph2 and SynCph1, superimposition of the GAF domains (r.m.s. deviation = 1.095 Å for 125 Cα); GAF1 and GAF2 of SynCph2 are displayed in orange and green; PAS, GAF, and PHY of SynCph1 in blue, gray, and pale red, respectively. The chromophores are shown in cyan (Cph2) and red (Cph1). The positions of the PRXSF, W(G/A)G, and WXE motifs in the tongue regions are conserved between SynCph1 and SynCph2, the residues are numbered along the SynCph2 count. C, tongue region of PaBphP (PDB code 3NHQ), the PAS (blue), GAF (gray) and PHY (red) domains and biliverdin in green. In contrast to SynCph2 and SynCph1 the tongue region consists of an extended loop region and α-helical elements. The spatial positions of the conserved motifs differ in PaBphP. The orientation of the tongue region correlates to that of SynCph2.