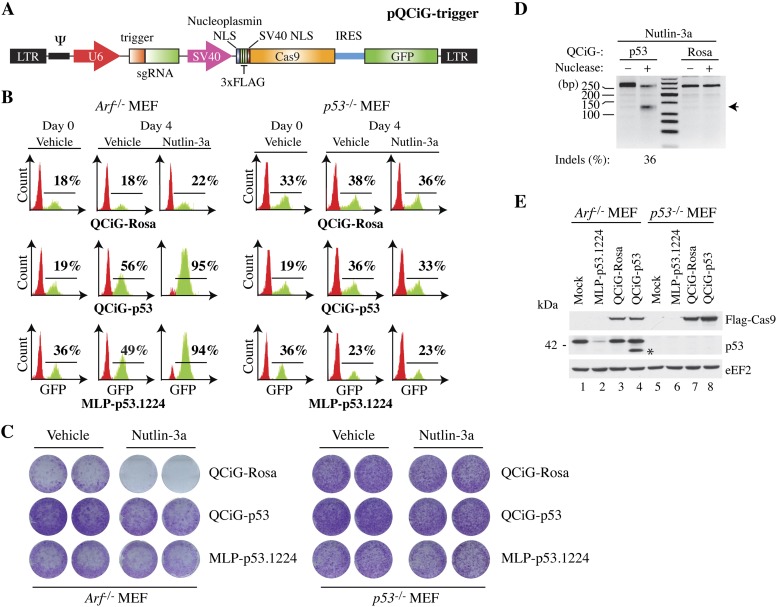
Figure 2.
Cas9-mediated editing of Trp53 in Arf−/− MEFs leads to Nutlin-3a resistance. (A) Schematic diagram of the pQ-based retroviral constructs driving expression of Cas9, GFP, and sgRNAs (pQCiG). (B) Flow cytometric analysis of Arf−/− and p53−/− MEFs transduced with QCiG-Rosa, QCiG-p53, or MLP-p53.1224 retroviruses, cultured 3 d later in the presence of vehicle or 10 μM Nutlin-3a for 24 h, and then allowed to recover for 4 d. (C) Colony formation assay of infected Arf−/− and p53−/− MEFs with QCiG-Rosa, QCiG-p53, or MLP-p53.1224. Five-thousand cells were seeded, exposed to 10 μM Nutlin-3a for 24 h, and allowed to recover for 12 d in the absence of drug, at which point they were stained with crystal violet. (D) SURVEYOR assay of DNA isolated from QCiG-p53- and QCiG-Rosa-infected Arf−/− MEFs exposed to 10 μM Nutlin-3a for 24 h and allowed to recover for 4 d. The arrowhead denotes the expected SURVEYOR cleavage products. (E) Immunoblot documenting Cas9 and p53 expression in QCiG- and MLP-infected MEFs. The asterisk denotes the position of a prominent p53 truncated product.