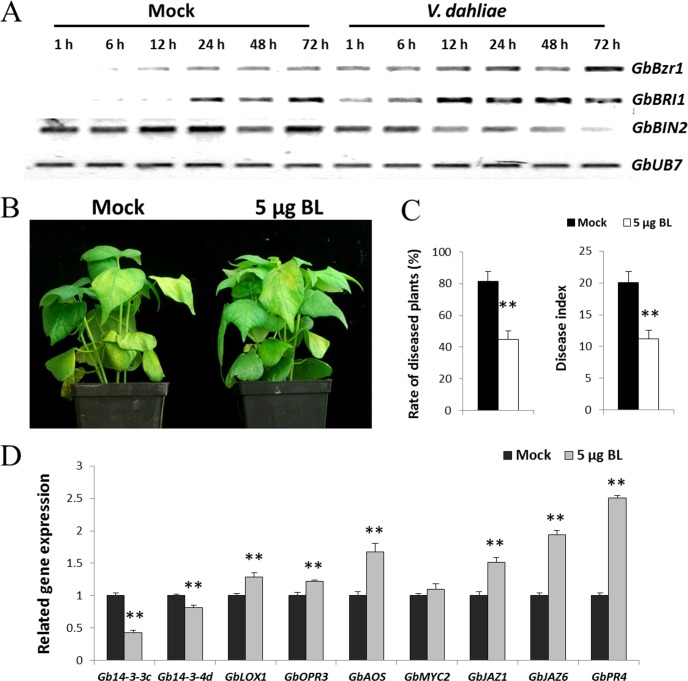
Fig. 5.
BL enhances disease resistance caused by V. dahliae in cotton. A, RT-PCR analysis of BR signaling pathway-related genes at the transcriptional level in G. barbadense cv7124 on inoculation with V. dahliae. PCR was performed by 28 cycles of amplification for GbUB7 and 29 cycles for other genes. BZR1, Brassinazole resistant 1; BRI1, Brassinosteroid insensitive 1; BIN2, Brassinosteroid insensitive 2. B, Effect of 5 μg/pot BL application on G. hirsutum cvYZ-1 seedlings inoculated with V. dahliae. Each experiment contains 16 plants and the experiment repeats for three times. Photograph of representative disease symptoms taken 9 d after inoculation. C, Rate of diseased plants and disease index of water- and BL-treated cotton plants. Plants were treated with BL by soil drenching 24 h before challenge inoculation with V. dahliae. The rate of diseased plants and disease index were measured at 4 d after the plants beginning to present disease symptoms. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates (n ≥ 16); asterisks indicate statistically significant differences, as determined by the Student t test (**p < 0.01). D, qPCR analysis of the Gb14-3-3c and Gb14-3-3d transcripts in control and BL treatments. JA signaling-related genes were detected at the transcriptional levels by qPCR. Error bars represent the standard deviation for three independent experiments, and three technical replicates were analyzed; asterisks indicate statistically significant differences, as determined by the Student t test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).