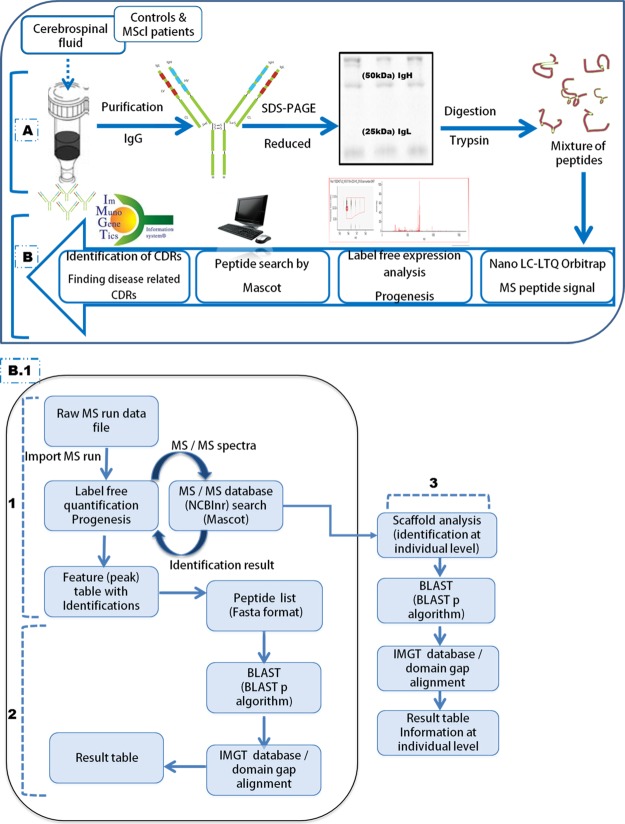
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of the proteomics-based methodology used to assign CDR presence exclusively in the CSF Ig of MScl patients. A, Ig was purified from the CSF of MScl patients (100 μl) and non-neurological controls (200 μl) based on the Ig concentration assay. Purification was performed using a Melon Gel IgG Spin Purification Kit. Purified Ig was separated into IgH and IgL chains via reducing one-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels. B, after in-gel trypsin digestion of excised IgH and IgL bands, the mixture of peptides was measured via nano-LC–LTQ-Orbitrap MS. Mass spectra were analyzed by Progenesis software, and the peptide search was performed by Mascot. Identified peptides were used for CDR identification using the IMGT database and BLASTp search algorithm to find MScl-specific CDRs. (1) Nano-LC–LTQ-Orbitrap MS-generated LC-MS profiles (raw MS run data) for the IgH and IgL datasets. These were analyzed separately using the Progenesis LC-MS software package (label-free quantification). Sequencing of the MS/MS spectra was executed via a Mascot MS/MS database search against the human subset of the NCBInr sequence database. Afterward, the identified peptides were imported into Progenesis and linked to their corresponding peaks. The peak abundance (UV area under the curve) information was used for analysis of CDR presence or absence. (2) Identified peptides were extracted and converted into FASTA format. They were aligned to V, D, J, and C elements of Ig (Homo sapiens) germline sequences derived from the IMGT database. We used the BLASTp search algorithm to align the identified peptide sequences to the corresponding Ig fragments. Next, they were submitted to the IMGT/domain gap alignment tool. This analysis provided alignment details of CSF Ig peptides relative to the Ig germline that included the gene name, homology match score, mutation/mismatch, and start and end positions. (3) Peptide identification details were uploaded in Scaffold. The Scaffold file contained a peptide identification view report based on the spectral counts (at MS/MS level). Peptide counts were obtained at the individual level for each sample and were exported to a spreadsheet containing detailed information about the protein and peptide hits. On the basis of the resulting combined peptide set, alignment summaries relative to the germline were assigned at the individual level (using a BLASTp algorithm and the IMGT database). This information was used for VH and VK family distribution analysis. BLAST, basic local alignment search tool; BLASTp, basic local alignment search tool for protein; IMGT, ImMunoGeneTics information system; Feature (or Peak), object of defined mass with an identified charge state, retention time, and isotopes characterized by the analysis software.