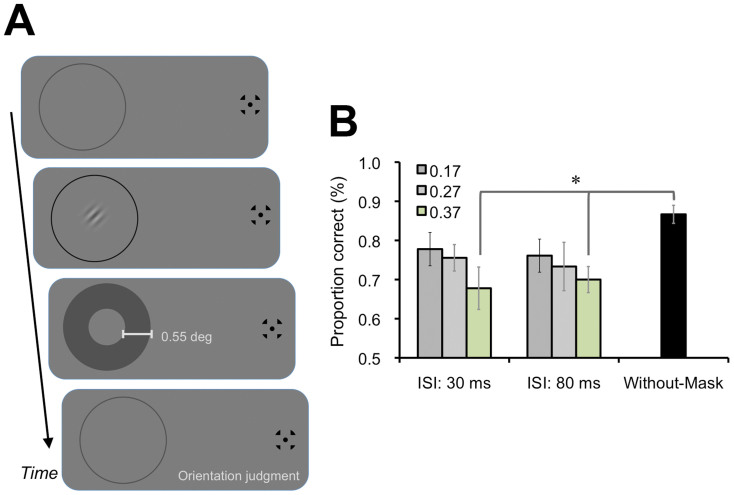
Figure 5. Visual metacontrast masking effect.
(A) In order to investigate what kind of visual stimuli could induce the suppression effect on visual perception comparable with the tactile suppression effect, we presented a visual masker (0.55 deg of width) instead of the tactile stimulus at a surrounding position of the visual target. The contrast of the visual masker was either 0.17, 0.27, or 0.37 (Weber contrast), and the ISI between visual target and masker was 30 ms or 80 ms. The Without-Mask condition was also included as a baseline. We introduced 240 main session trials (Mask Conditions (2) × Mask contrasts (3) × ISIs (2) × Target's orientations (2) × Repetitions (10)), followed by 72 training session trials (3 Repetitions). Except for these differences, the stimulus, apparatus, and procedure were identical to those used in Exps. 2–4. (B) Results. The one-way repeated measures ANOVA found a significant main effect of the conditions [F(6, 48) = 3.14, p < .05]. The post hoc test revealed that the proportions of correct responses for visual discrimination in the conditions with 0.37 of contrast and with 30 ms and 80 ms of ISI were significantly lower than in the Without-Mask condition (p < .05). Error bars denote the standard error of the mean (N = 9). An asterisk indicates the conditions with a significant difference (p < .05).