Fig. 3.
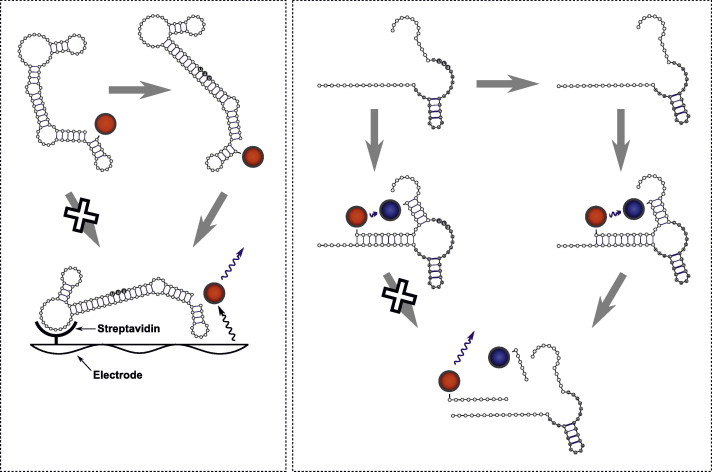
RNA editing assays that are developed for high-throughput screening – Left panel illustrates the RNA aptamer-based assay. In this assay, an aptamer that is labeled with ruthenium (red ball) is used, which upon successful addition of three Us changes conformation and, becomes activated, and thus binding to the streptavidin that coats the microtiter plate. Upon electrical stimulation, the ruthenium complex generates a measurable ECL signal. Right panel illustrates the FRET-based assay, in which the 16nt-long reporter RNA is labeled with a fluorescent reporter (FAM, red ball) and a fluorescent quencher (TAMRA, blue ball). In this assay, upon successful deletion of three Us from the catalytic core of HHR, the inactive HHR becomes active and cleaves the reporter RNA and generates a detectable fluorescent signal. (For interpretation of reference to colors in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
