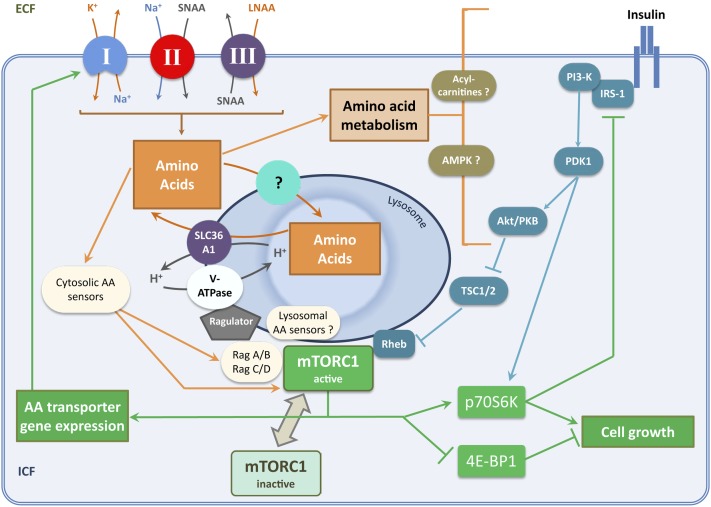
FIGURE 3.
Neutral AA transporters and activation of the mTORC1 signaling pathway. This diagram shows the relation between neutral AA transport, intracellular AA concentration, and the mTORC1 growth signaling pathway in nonepithelial mammalian cells (see text for further details). A sequential relation between primary, secondary, and tertiary active transport systems (denoted as “I,” “II,” and “III,” respectively) contributes substantially to transport of LNAAs across cell membranes. Energy input is provided through ATP hydrolysis by the Na+/K+ pump (primary active transport). Note the operation of symport (cotransport) and antiport (exchange) mechanisms for AAs in series downstream of the Na+/ K+ pump. In epithelial cells, broad-scope neutral AA transporters provide both SNAAs and LNAAs coupled to ion fluxes by secondary active transport, lessening the requirement for step III. AA (principally LNAA) concentration and/or flux within intracellular compartments promotes recruitment of mTORC1 to lysosomes where it is activated by interactions with Rag and Rheb GTPases. Such activation of mTORC1, downstream of nutrient (AA) and growth factor (insulin) signals, stimulates protein synthesis and ribosome biogenesis by effector mechanisms as indicated. Both cytosolic and lysosomal AA sensors have been reported (see sections in text entitled “Plasma membrane AA transporters and cytosolic AA sensing upstream of mTORC1” and “AA transporters and lysosomal AA sensing upstream of mTORC1”). Remarkably little is known about the transporter or transporters mediating neutral AA uptake into lysosomes, although SLC38A7 has recently emerged as a candidate for this role (48). Intracellular AA metabolism may also modulate growth factor signaling upstream of mTORC1 (62, 63). AA, amino acid; Akt/PKB, protein kinase B; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; ECF, extracellular fluid; ICF, intracellular fluid; IRS-1, insulin receptor substrate 1; LNAA, large neutral amino acid; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; PDK1, 3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase 1; PI3-K, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; Rag, Ras-related GTPase; Rheb, Ras homolog enriched in brain; SLC36A1, solute carrier 36A1; SNAA, small neutral amino acid; TSC1/2, tuberous sclerosis complex 1/2; V-ATPase, vacuolar H+-ATPase; 4E-BP1, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E binding protein 1.