Figure 3. Evaluation of the effect of ar-turmerone on mouse motor function and balance.
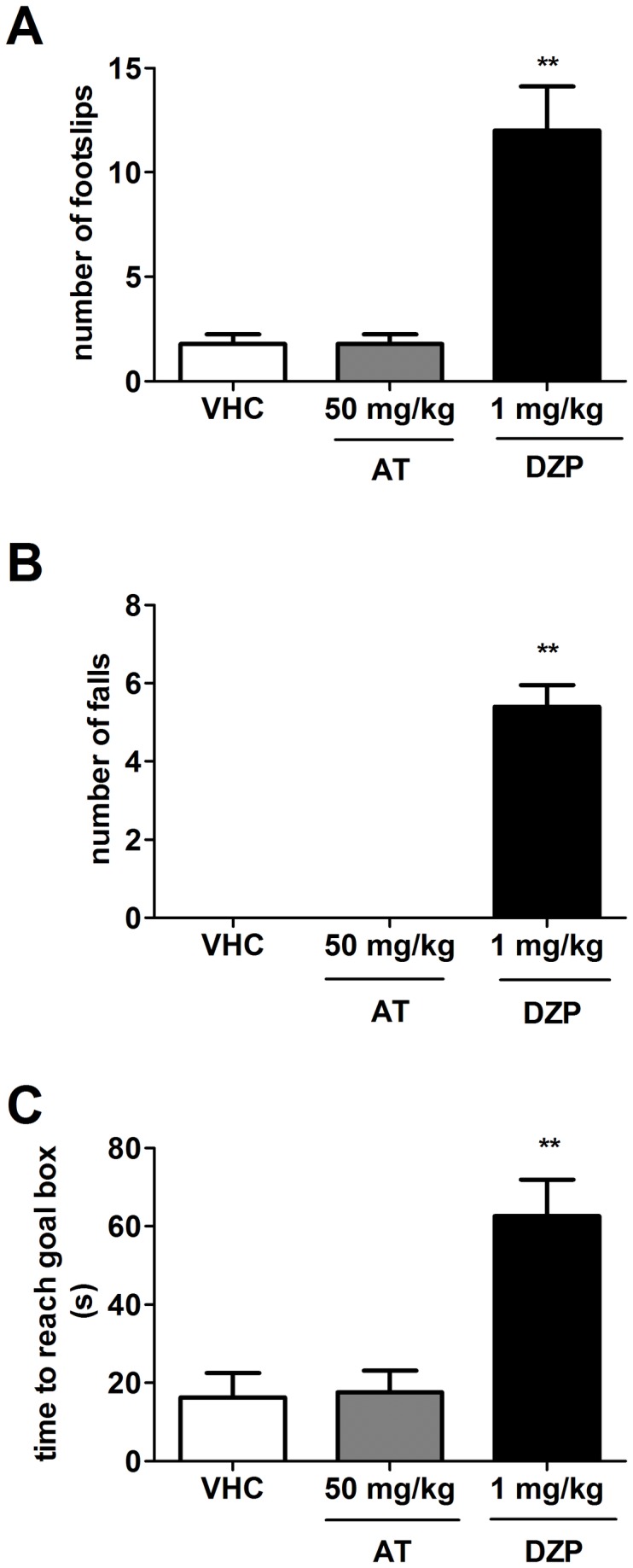
An intravenous dose of 50 mg/kg of ar-turmerone (AT) does not cause any alteration of motor skills in mice. Sensitivity of this model was confirmed by detection of motor and balance deficits induced by diazepam (DPZ) in mice at 1 mg/kg. Compared to control group (VHC), DZP-treated mice displayed a significant increase in number of footslips (A), falls (B) and time to reach goal box (C). Statistically significant differences between control and sample groups are labeled as ** for p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA test).
