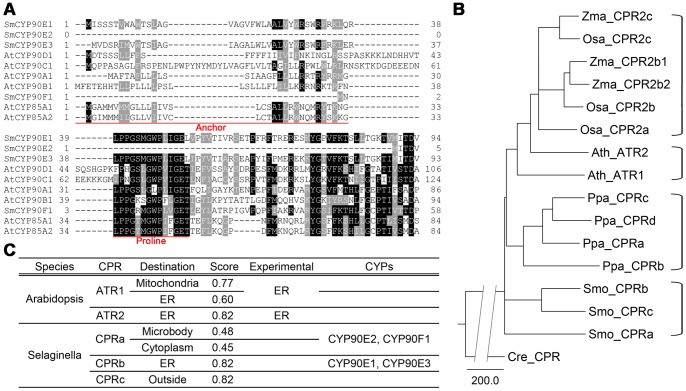
Figure 2. Predicted subcellular localization of CYPs and their putative reductases.
(A) Multiple sequence alignment of CYP amino acid sequences from Selaginella and Arabidopsis. Sequences corresponding to functional domains identified in AtCYP90B1 are underlined. Box shading was carried out using BOXSHADE 3.21. Dashes represent gaps. Letters in black and gray backgrounds indicate 100% and 50% conservation among the sequences, respectively. The N-terminal regions up to the first 124 amino acids are shown. (B) Prediction of the subcellular localization of the NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductases (CPRs). The PSORT program was used to predict and score the calculation. (C) Phylogenetic tree of CPRs from Arabidopsis, maize, rice, Physcomitrella, and Selaginella. CPRs from the same species or from Zea mays (Zm) and Oryza sativa (Os) combined are bracketed on the right. The Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CPR sequence was used as an outgroup. The broken line for the outgroup indicates a genetic distance of 400. Scale bar = genetic distance of 200.